AutoEncoder
AutoEncoder
-
오토인코더(
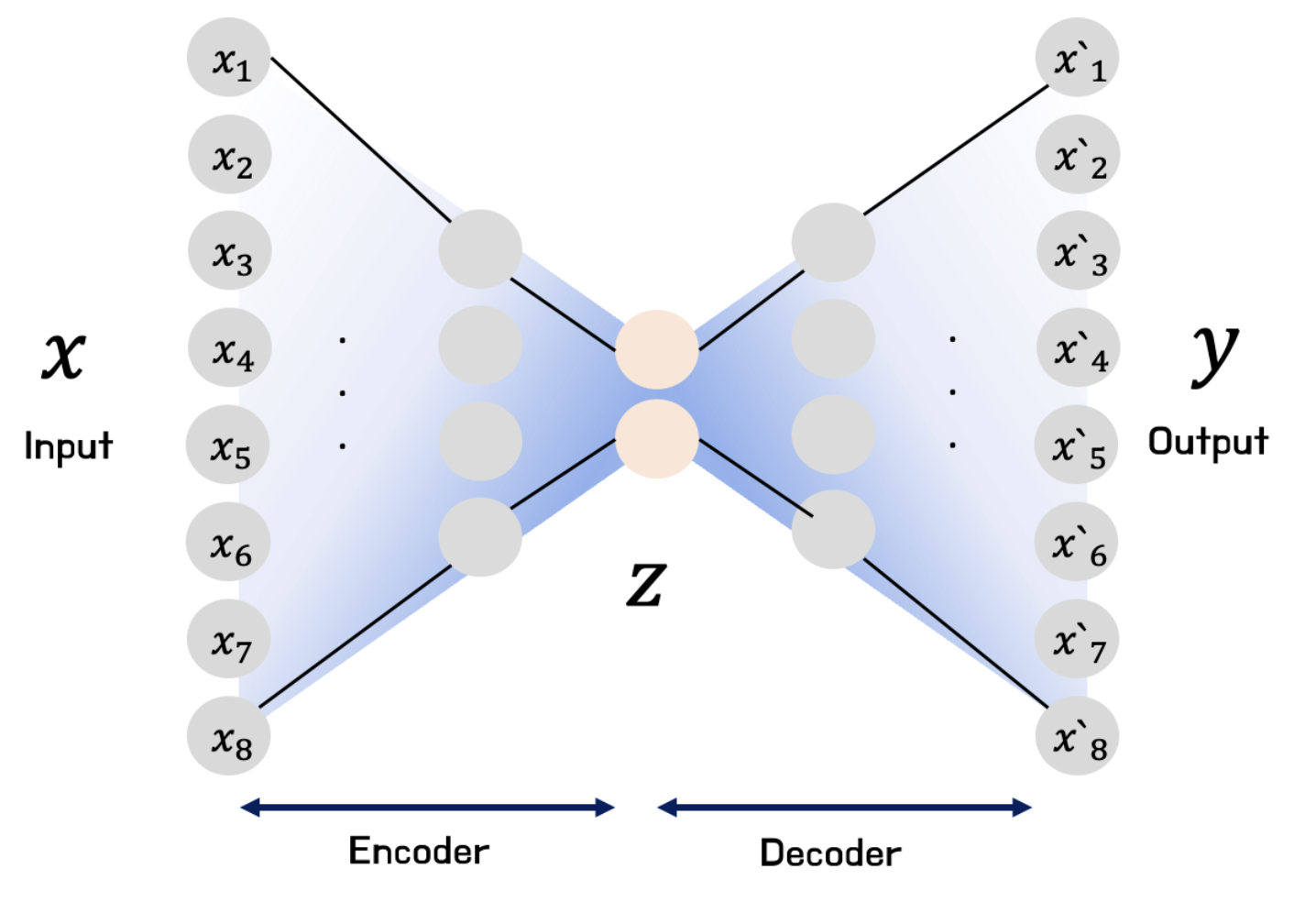
\[X \xrightarrow{\text{Encoder}} Z \xrightarrow{\text{Decoder}} \hat{X}\]AutoEncoder; AE) : 입력 데이터를 압축시켜 저차원 특징 공간으로 축소한 후, 이를 다시 확장하여 원본으로 복원하는 인공신경망 아키텍처 -
Encoder:
\[\begin{aligned} \mathbf{z} = F\left(\mathbf{x} ; \Theta \right) \end{aligned}\]- \(F_{\Theta}\) : Encoder Layer
- \(\mathbf{x}\) : Input Data
- \(\mathbf{z}\) : Latent Space
-
Decoder:
\[\begin{aligned} \hat{\mathbf{x}} = G\left(\mathbf{z} ; \Phi \right) \end{aligned}\]- \(G_{\Phi}\) : Encoder Layer
- \(\mathbf{z}\) : Latent Space
- \(\hat{\mathbf{x}}\) : Output Data
-
Optimization:
\[\begin{aligned} \hat{\mathbf{z}}, \hat{\Theta}, \hat{\Phi} &= \text{arg}\min{\mathcal{L}\left(\mathbf{x}, \hat{\mathbf{x}}\right)} \end{aligned}\]
Variations
-
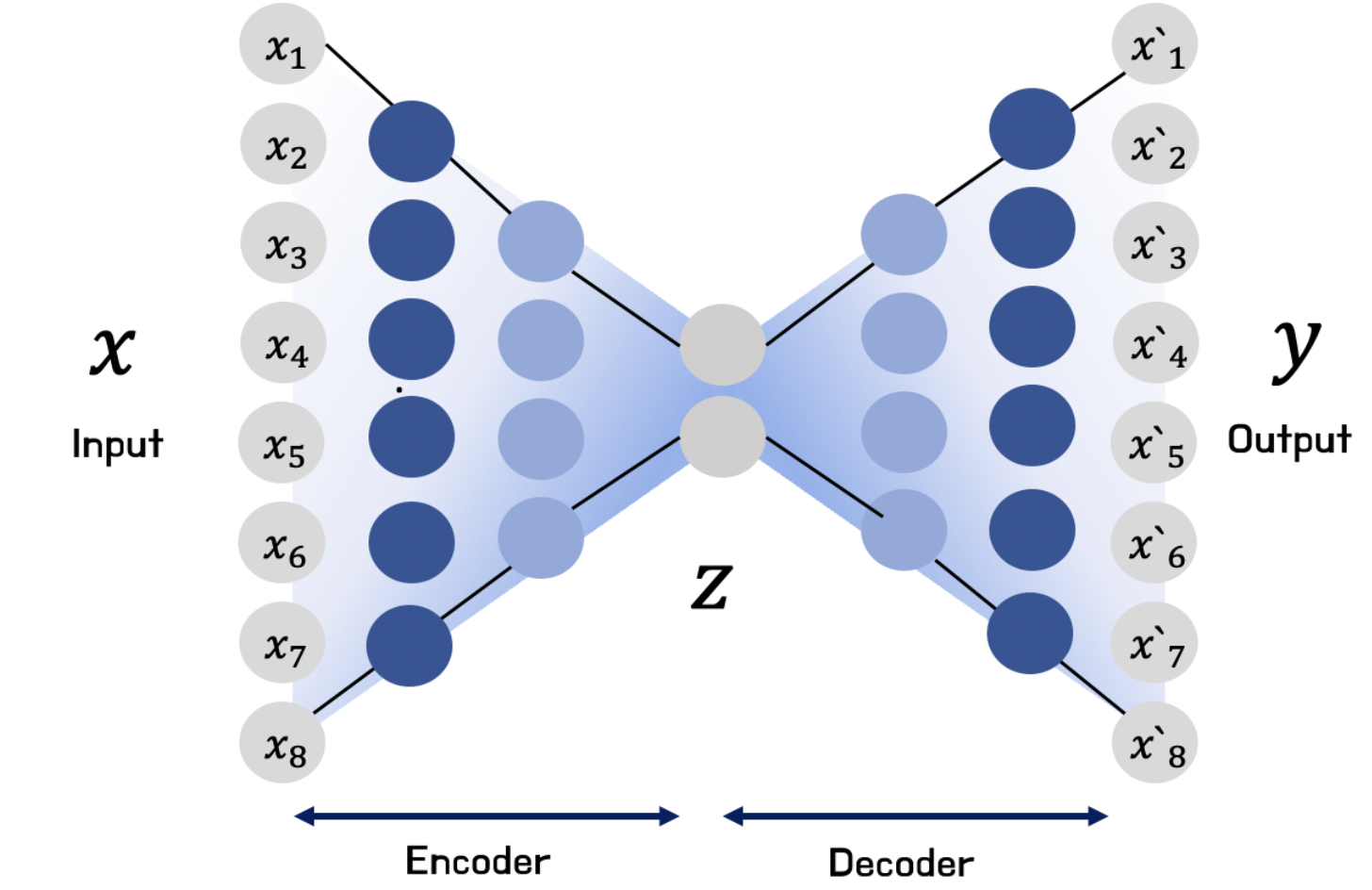
적층 오토인코더(Stacked AutoEncoder or Deep AutoEncoder) : 입력층과 잠재공간, 잠재공간과 출력층 사이에 여러 장의 은닉층을 추가함으로써 기본 오토인코더보다 복잡하고 비선형적인 데이터 패턴을 잘 포착하도록 함
-
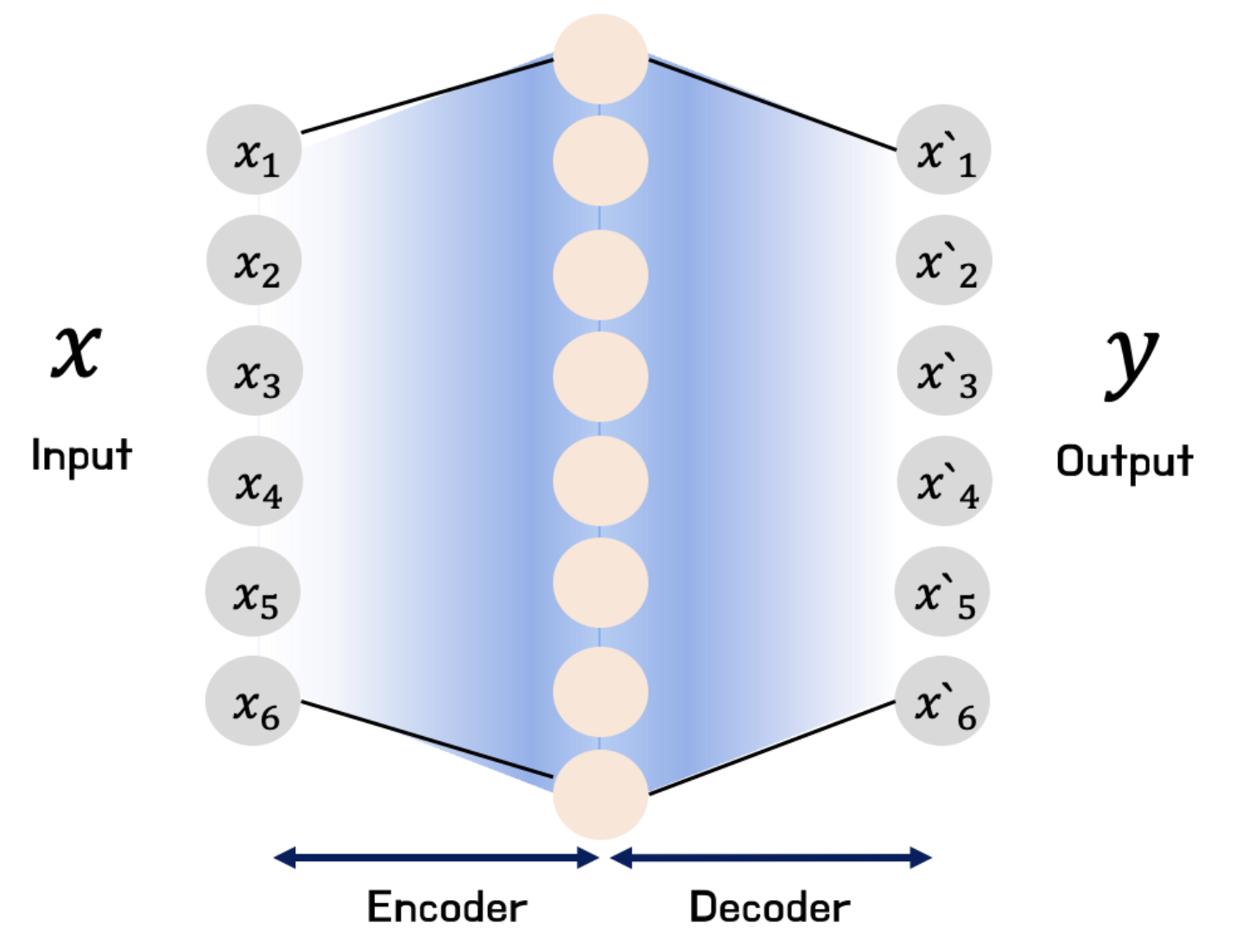
희소 오토인코더(
SparseAutoEncoder; SAE) : 입력 데이터를 고차원으로 확장했다가 본래 차원으로 축소하는 과정을 통해 저차원에서는 발견하기 어려운 잠재 정보나 패턴을 포착하도록 함-
희소성 제약(Sparse Constraint) : 특히 Sparse AutoEncoder 에서, 데이터 과적합을 방지하고 핵심 정보만 선택적으로 학습하기 위하여 은닉층 뉴런 중 일부만 활성화되도록 강제하는 기법
\[\begin{aligned} \mathcal{L}=\frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^{N}{\Vert \mathbf{x}_{i} - \hat{\mathbf{x}}_{i} \Vert^{2}} + \beta \cdot \underbrace{\Omega(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}} \mid m, \rho)}_{\begin{array}{c} \text{Sparse} \\ \text{Penalty} \end{array}} \end{aligned}\] -
Sparse Penalty Function : 은닉층 뉴런들이 평균적으로 목표 희소성 비율에 가깝게 활성화되도록 하기 위함으로, 대개 쿨백 라이블러 발산(Kullback–Leibler Divergence)을 활용함
\[\begin{aligned} \Omega(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}} \mid m, \rho) &= \sum_{j=1}^{m}{D_{KL}\left[\rho \parallel \hat{\rho}_{j}\right]}\\ &= \sum_{j=1}^{m}{\rho \cdot \log{\frac{\rho}{\hat{\rho}_{j}}} + (1-\rho) \cdot \log{\frac{1-\rho}{1-\hat{\rho}_{j}}}} \end{aligned}\]- $m$ : 은닉층 뉴런 수
- $\rho$ : 목표 희소성 비율
- \(\hat{\rho}_{j}=\displaystyle\frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^{N}{h_{j}^{(i)}}\) : 은닉층 뉴런 $j$ 의 평균 출력값
-
-
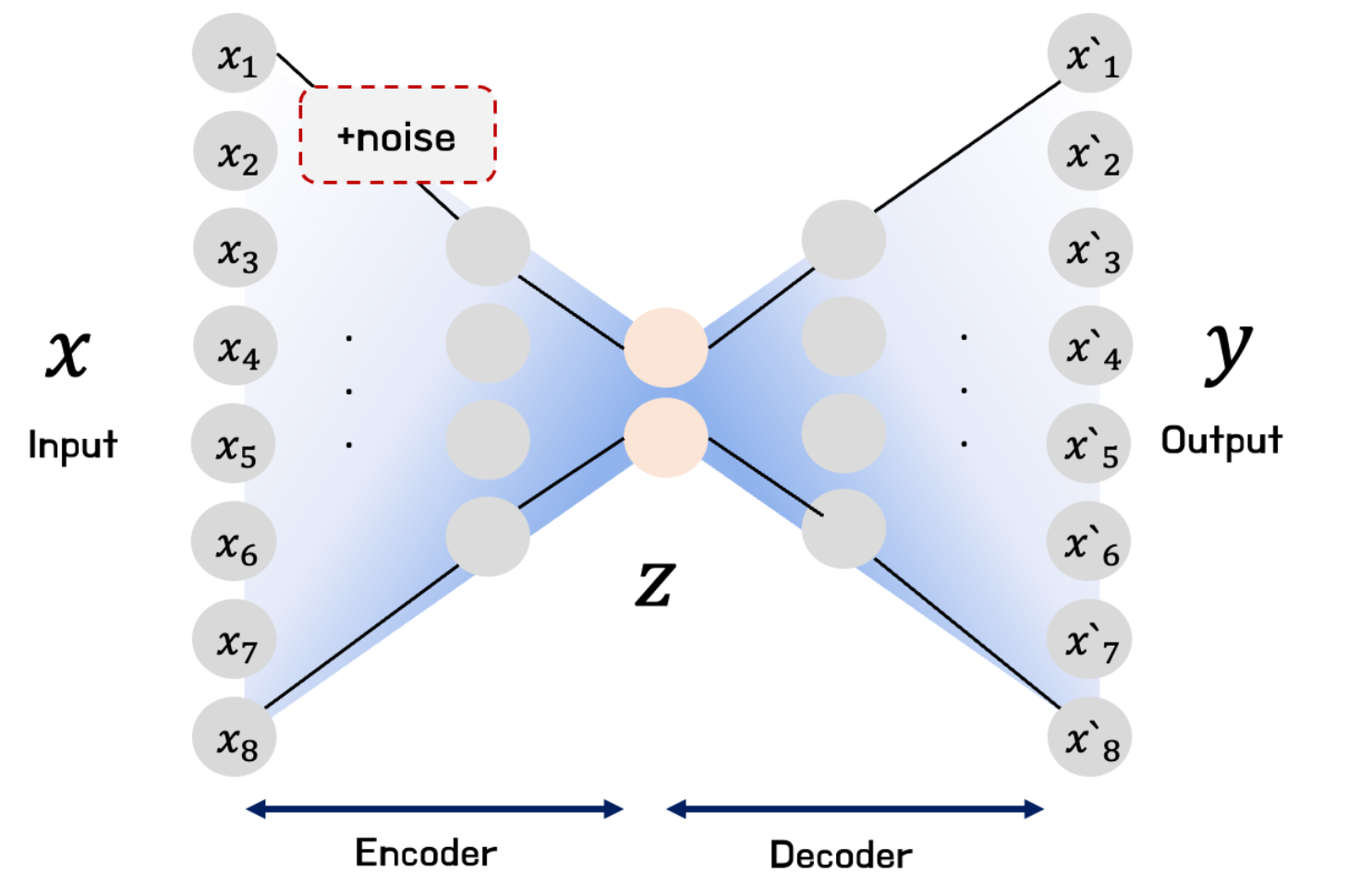
잡음 제거 오토인코더(
DenoisingAutoEncoder; DAE) : 원본 데이터에 잡음을 추가하여 입력한 후, 원본을 복원함으로써 잡음에 대한 강건성을 확보하고 데이터의 본질적인 특징에 집중할 수 있도록 함-
How to Generate Noise
\[\begin{aligned} \tilde{\mathbf{x}} &= g(\mathbf{x} \mid \theta) \end{aligned}\]-
Gaussian Noise:
\[\begin{aligned} g(\mathbf{x} \mid \sigma)= \mathbf{x} + \epsilon, \quad \epsilon \sim \mathcal{N}(0,\sigma^2) \end{aligned}\] -
Salt and Pepper Noise:
\[g(\mathbf{x} \mid p)=\begin{cases}\begin{aligned} \mathbf{x} \quad & 1-p\\ \mathbf{v}_{\text{min}} \quad & \frac{p}{2}\\ \mathbf{v}_{\text{max}} \quad & \frac{p}{2} \end{aligned}\end{cases}\] -
Masking Noise:
\[\begin{aligned} g(\mathbf{x} \mid p)= \mathbf{x} \cdot m, \quad m \sim \text{Bernouli}(1-p) \end{aligned}\]
-
-
Source
- https://velog.io/@jochedda/%EB%94%A5%EB%9F%AC%EB%8B%9D-Autoencoder-%EA%B0%9C%EB%85%90-%EB%B0%8F-%EC%A2%85%EB%A5%98