Attention Mechanism
Based on the lecture “Text Analytics (2024-1)” by Prof. Je Hyuk Lee, Dept. of Data Science, The Grad. School, Kookmin Univ.
Attention Mechanism
- 어텐션 메커니즘(Attention Mechanism) : 요청 정보와 참조 정보가 주어진 상황에서, 특정 요청 정보가 입력되었을 때 해당 요청 정보와 각 참조 정보 간 매칭 점수를 토대로 참조 정보를 가중합한 문맥 정보를 생성하는 메커니즘
- 교차 어텐션(Cross Attention) : 입력값과 반환할 값이 다른 경우
- 셀프 어텐션(Self Attention) : 입력값과 반환할 값이 같은 경우
-
Framework
\[\begin{aligned} \text{ATTN}\left(\mathcal{Q},\mathcal{K},\mathcal{V}\right) = \text{Softmax}\left[f(\mathcal{Q},\mathcal{K})\right] \cdot \mathcal{V} = \mathcal{C} \end{aligned}\]- INPUT
- \(\mathcal{Q} \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times D}\) : 요청 정보로서 질의(Query)
- \(\mathcal{K} \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times D}\) : 요청 정보와의 매칭 점수 계산에 동원되는 참조 정보의 인덱스로서 키(Key)
- \(\mathcal{V} \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times D_{V}}\) : 참조 정보의 인덱스가 가리키는 실제 정보로서 값(Value)
- OUTPUT
- \(\mathcal{A}=f(\mathcal{Q},\mathcal{K}) \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times N}\) : 질의와 키 간 유사도 행렬
- \(\alpha_{m,n} \in \mathcal{A}\) : 어텐션 점수(Attention Score)
- \(\mathcal{W}=\text{Softmax}\left[\mathcal{A}\right] \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times N}\) : 유사도 정규화 행렬로서 어텐션 맵(Attention Map)
- \(\omega \in \mathcal{W}\) : 어텐션 분포(Attention Distribution)
- \(\omega_{m,n} \in \omega \in \mathcal{W}\) : 어텐션 가중치(Attention Weight)
- \(\mathcal{C}=\mathcal{W} \cdot \mathcal{V} \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times D_{V}}\) : 문맥 행렬(Context Matrix)
- \(\sigma \in \mathcal{C}\) : 문맥 벡터(Context Vector)
- \(\mathcal{A}=f(\mathcal{Q},\mathcal{K}) \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times N}\) : 질의와 키 간 유사도 행렬
- INPUT
-
Attention Score Function
Name Function Defined by Dot Product \(f(\mathbf{q}, \mathbf{K}) = \mathbf{q} \cdot \mathbf{K}\) Luong et al. (2015) Learnable Weighted Attention \(f(\mathbf{q}, \mathbf{K}) = \mathbf{q}^{T} \cdot \mathbf{W} \cdot \mathbf{K}\) Luong et al. (2015) Additive Attention \(f(\mathbf{q}, \mathbf{K}) = \mathbf{W}^{T}_{A} \cdot \text{tanh}\left[\mathbf{W}_{B} \cdot (\mathbf{q} \oplus \mathbf{K})\right]\) Bahdanau et al. (2015) Concatenation \(f(\mathbf{q}, \mathbf{K}) = \mathbf{W}^{T}_{A} \cdot \text{tanh}\left[\mathbf{W}_{B} \cdot \mathbf{q} + \mathbf{W}_{C} \cdot \mathbf{K}\right]\) Bahdanau et al. (2015) Scaled Dot Product \(f(\mathbf{q}, \mathbf{K}) = \displaystyle\frac{\mathbf{q}^{T} \cdot \mathbf{K}}{\sqrt{n}}\) Vaswani et al. (2017)
Adaptive Weight
-
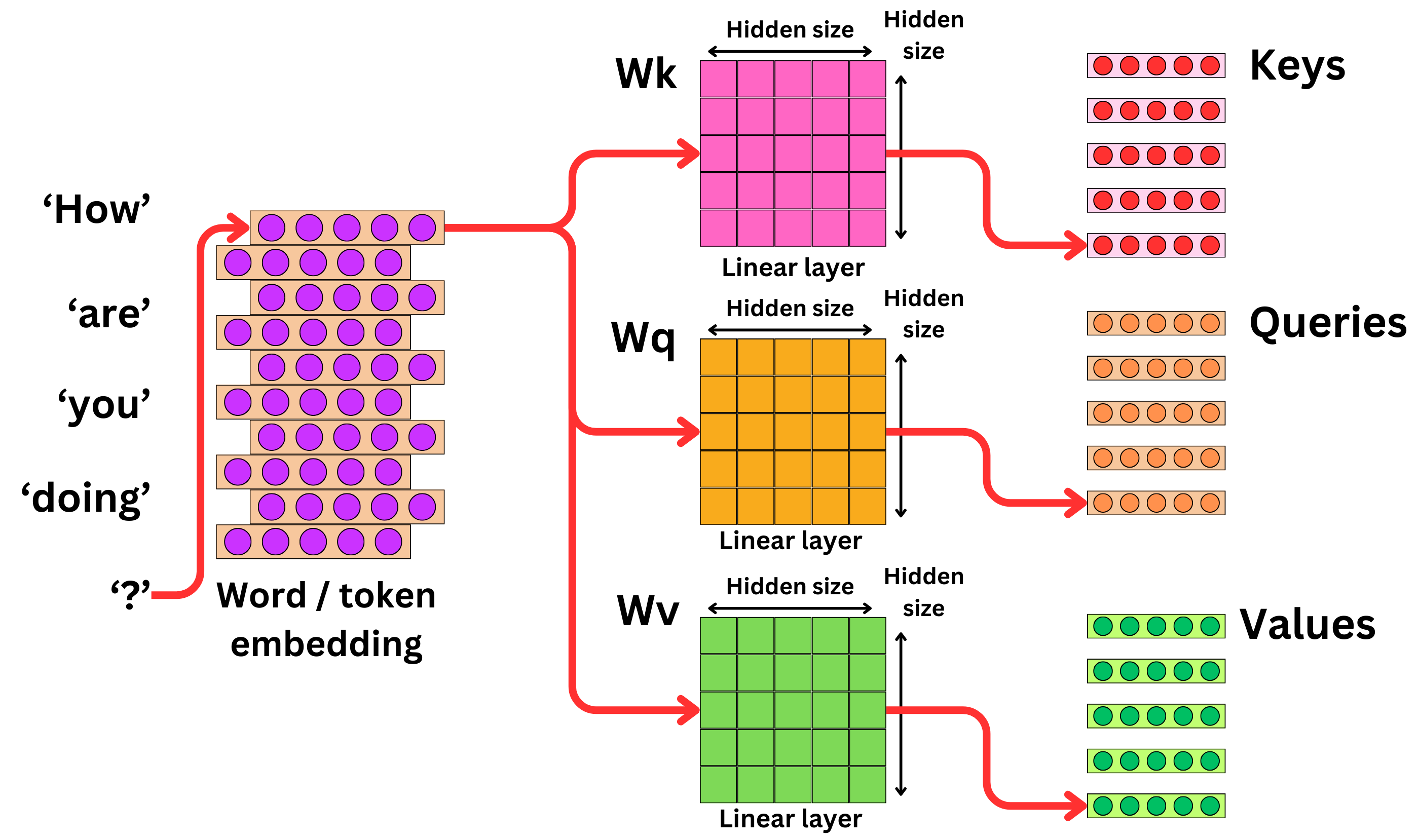
적응형 가중치 할당(Adaptive Weight Allocation) : 표현력을 강화하기 위하여 학습 가능한 가중치 행렬 $\mathbf{W}$ 을 활용하여 $\mathcal{Q}, \mathcal{K}, \mathcal{V}$ 를 선형 변환하고, 이를 기반으로 유사도를 계산하여 입력 간 상호작용 정보를 동적으로 학습하는 기법
WHAT INPUT DATA LEARNABLE WEIGHT TOTAL \(\mathcal{Q}\) \(\mathbf{Q} \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times D_{Q}}\) \(\mathbf{W}_{Q} \in \mathbb{R}^{D_{Q} \times D}\) \(\mathbf{Q} \cdot \mathbf{W}_{Q} \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times D}\) \(\mathcal{K}\) \(\mathbf{K} \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times D_{K}}\) \(\mathbf{W}_{K} \in \mathbb{R}^{D_{K} \times D}\) \(\mathbf{K} \cdot \mathbf{W}_{K} \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times D}\) \(\mathcal{V}\) \(\mathbf{V} \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times D_{V}}\) \(\mathbf{W}_{V} \in \mathbb{R}^{D_{V} \times D}\) \(\mathbf{V} \cdot \mathbf{W}_{V} \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times D}\) -
WHY? NECESSITY
- $\mathcal{Q}, \mathcal{K}, \mathcal{V}$ 간 차원 보정이 필요한 경우
- $\mathcal{Q}$ 와 $\mathcal{K}$ 가 서로 다른 특징 차원을 가지고 있는 경우($D_{Q} \ne D_{K} \ne D_{V}$)
- $\mathcal{Q}$ 와 $\mathcal{K}$ 가 서로 같은 특징 차원을 공유하고 있으나 상황에 따라 유사도가 중요도에 작용하는 방향(선호/비선호)이 다를 경우
- 상호작용 정보를 포착함에 있어서 유사도 이상의 복잡한 관계를 조명하고자 하는 경우
- 셀프 어텐션에서, 입력값과 반환할 값은 동일하나 역할($\mathcal{Q}, \mathcal{K}, \mathcal{V}$)에 따라 서로 다른 정보 처리를 수행해야 하는 경우
- 멀티 헤드 어텐션에서, 헤드마다 상호작용 정보를 다각도로 포착하고자 하는 경우
- $\mathcal{Q}, \mathcal{K}, \mathcal{V}$ 간 차원 보정이 필요한 경우
Variations
-
멀티 헤드 어텐션(Multi-Head Attention) : 입력 데이터를 여러 독립적인 적응형 가중 어텐션 메커니즘(헤드)으로 병렬 처리하여, 데이터 간 관계와 패턴을 다각도로 학습하는 기법
-
하나의 헤드는 독립적인 적응형 가중 어텐션으로 이루어짐
\[\begin{aligned} \text{HEAD}^{(h)} &= \text{ATTN}^{(h)}\left(\mathbf{Q} \cdot \mathbf{W}_{\mathcal{Q}}^{(h)}, \mathbf{K} \cdot \mathbf{W}_{\mathcal{K}}^{(h)}, \mathbf{V} \cdot \mathbf{W}_{\mathcal{V}}^{(h)}\right) \end{aligned}\] -
멀티 헤드 어텐션의 결과값은 헤드별 결과값의 벡터 결합을 선형 변환한 값임
\[\begin{aligned} \text{Multi-Head}\left(\mathbf{Q}, \mathbf{K}, \mathbf{V}\right) &= \left[\cdots \oplus \text{HEAD}^{(h)} \oplus \cdots \right] \cdot \mathbf{W}_{\mathcal{O}} \end{aligned}\]
-
-
셀프 어텐션(Self-Attention) : 입력값과 반환할 값이 같은 경우로서, 통상 역할($\mathcal{Q}, \mathcal{K}, \mathcal{V}$)에 따라 서로 다른 정보 처리를 수행하도록 적응형 가중 어텐션과 결합되어 활용됨
\[\begin{aligned} \mathcal{Q}=\mathbf{X} \cdot \mathbf{W}^{(Q)}, \quad \mathcal{K}=\mathbf{X} \cdot \mathbf{W}^{(K)}, \quad \mathcal{Q}=\mathbf{V} \cdot \mathbf{W}^{(V)} \end{aligned}\] -
마스크 행렬(Mask Matrix) : 특정 위치에 대한 가중치를 차단하거나 조정함으로써 예측해야 하는 정보가 유출되거나 불필요한 정보가 참조되는 것을 방지함
\[\begin{aligned} f\left(\mathcal{Q}_{M \times D}, \mathcal{K}_{N \times D}\right) + \mathbf{M}_{M \times N} \end{aligned}\]- 셀프 어텐션은 입력 데이터의 모든 위치가 서로 영향을 주고받는 구조이나, 시퀀스 생성 모형은 현재 순번 데이터로만 다음 순번을 예측해야 하므로, 미래 위치에 대한 주의 점수를 $-\infty$ 로 처리하여 모형이 해당 정보를 참조하지 못하도록 강제함
Application to SEQ2SEQ
-
SEQ2SEQ 적용 목적 : RNN 계열 레이어의 초기 순번 정보 유실 문제 및 기울기 소실 문제를 보완하기 위함으로서, 문맥 벡터를 최종 은닉 상태로 획일화하여 사용하지 않고, 인코더 각 순번 은닉 상태와 디코더 현재 시점 간 관련성을 고려하여, 디코더의 각 시점에 특화된 문맥 벡터를 생성함
-
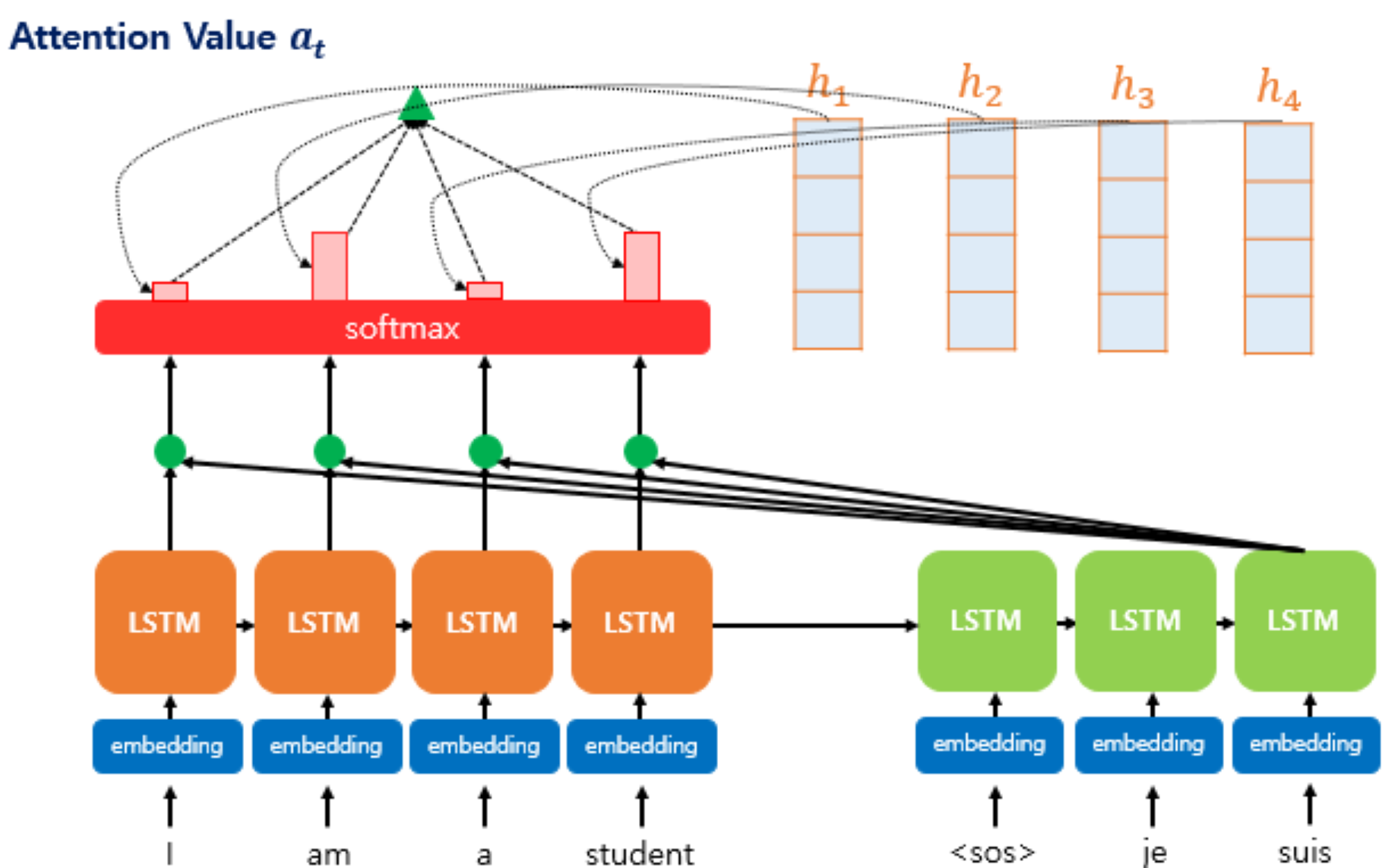
루옹 어텐션(Luong Attention) : 디코더의 현재 시점 은닉 상태를 활용하여 문맥 벡터를 생성하고, 이를 현재 시점 은닉 상태에 적용하는 어텐션 기법
-
Attention Mechanism
\[\sigma^{(t)} = \text{ATTN}\left(\eta_{t}, \mathbf{H}, \mathbf{H}\right)\]- \(\mathcal{Q} = \eta_{t}\) : 디코더의 $t$ 시점 은닉 상태
- \(\mathcal{K} = \mathcal{V} = \mathbf{H}\) : 인코더의 각 순번 은닉 상태 행렬
- \(\sigma^{(t)}\) : 디코더의 $t$ 시점 문맥 벡터(Context Vector)
-
Combining information on the context vector at $t$ and the hidden state at $t$
\[\mathbf{z}_{t} = \text{F}_{\text{tanh}}\left[\sigma^{(t)} \oplus \eta_{t}\right]\]
-
-
바다나우 어텐션(Bahdanau Attention) : 디코더의 이전 시점 은닉 상태를 활용하여 문맥 벡터를 생성하고, 이를 현재 시점 입력값에 적용하는 어텐션 기법
-
Attention Mechanism
\[\sigma^{(t)} = \text{ATTN}\left(\eta_{t-1}, \mathbf{H}, \mathbf{H}\right)\]- \(\mathcal{Q} = \eta_{t-1}\) : 디코더의 $t-1$ 시점 은닉 상태
- \(\mathcal{K} = \mathcal{V} = \mathbf{H}\) : 인코더의 각 순번 은닉 상태 행렬
- \(\sigma^{(t)}\) : 디코더의 $t$ 시점 문맥 벡터(Context Vector)
-
Combining information on the context vector at $t$ and the input vector at $t$
\[\mathbf{z}_{t} = \sigma^{(t)} \oplus \hat{\mathbf{y}}_{t-1}\]
-
Sourse
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/what-self-attention-impact-large-language-models-llm-nikhil-goel-srpbc
- https://newsletter.theaiedge.io/p/the-multi-head-attention-mechanism
- https://krypticmouse.hashnode.dev/attention-is-all-you-need
- https://wikidocs.net/22893
- https://wikidocs.net/73161