AutoRec
Based on the following lectures
(1) “Recommendation System Design (2024-1)” by Prof. Ha Myung Park, Dept. of Artificial Intelligence. College of SW, Kookmin Univ.
(2) "Recommender System (2024-2)" by Prof. Hyun Sil Moon, Dept. of Data Science, The Grad. School, Kookmin Univ.
AutoRec
- 문제 의식
RBM-CF(RestrictedBoltzmannMachines forCollaborativeFiltering): 확률적 생성 모형으로서, 평점값마다 별도의 파라미터를 설정하므로 학습 파라미터 수가 급증하고, 확률 생성 과정을 근사 학습하므로 수렴 속도가 느림LLORMA(LocalLow-RankMatrixApproximation): 행렬분해 기반 잠재요인 모형으로서, 사용자 취향이 전역적으로 일관되지 않을 수 있다는 전제 하에 사용자-아이템 상호작용 행렬을 다수의 하위 행렬로 재구성하고, 각각을 지역적 저차원(Local Low Rank)으로 근사하나, 구조가 복잡함
AutoRec: 오토인코더 기반 협업필터링 모형으로서, 연속적 출력값을 결정론적 함수로 도출하는 단일 신경망 구조를 통해 선행 협업필터링 모형에 비해 계산 효율성과 구조적 간결성을 도모함- Sedhain, S., Menon, A. K., Sanner, S., & Xie, L.
(2015, May).
Autorec: Autoencoders meet collaborative filtering.
In Proceedings of the 24th international conference on World Wide Web (pp. 111-112).
- Sedhain, S., Menon, A. K., Sanner, S., & Xie, L.
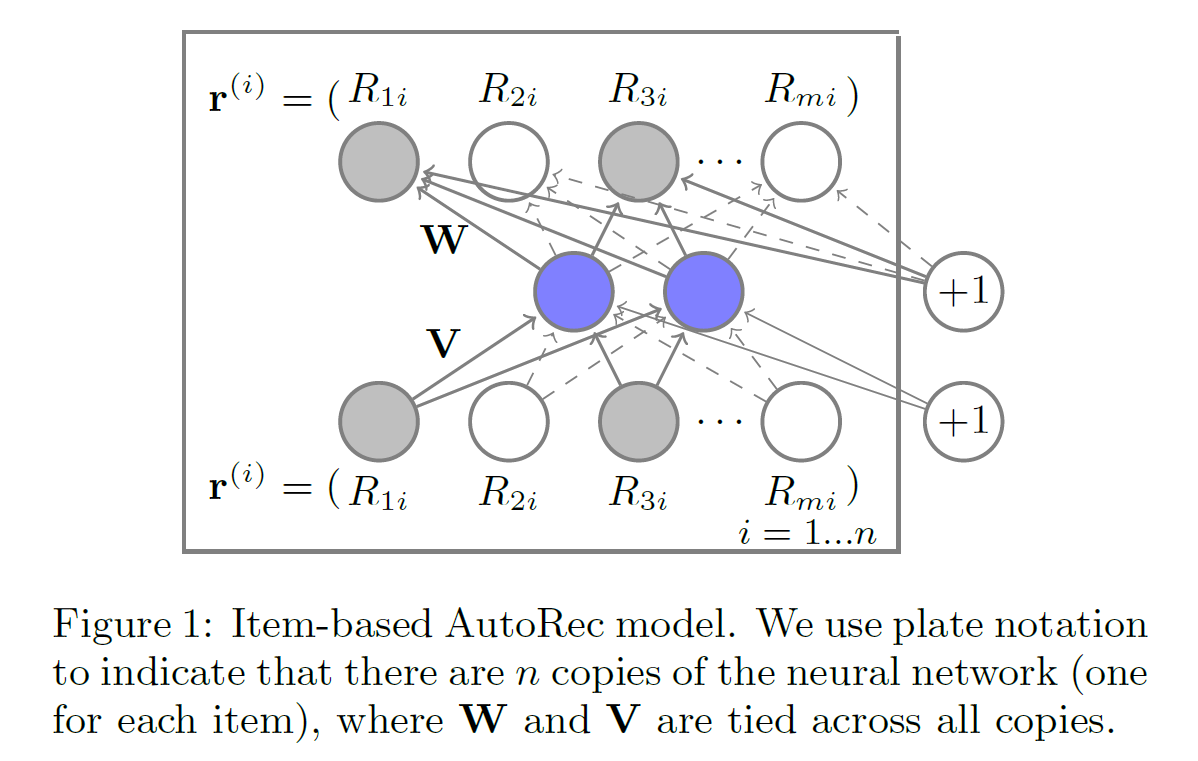
Notation
- $u=1,2,\cdots,M$: user idx
- $i=1,2,\cdots,N$: item idx
- $\mathbf{R} \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times N}$: user-item explicit feedback matrix
- $\mathbf{V} \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times K}$: linear transformation matrix @ encoder
- $\mathbf{W} \in \mathbb{R}^{K \times M}$: linear transformation matrix @ decoder
- $\overrightarrow{\beta} \in \mathbb{R}^{K}$: bias vector @ encoder
- $\overrightarrow{\mathbf{b}} \in \mathbb{R}^{M}$: bias vector @ decoder
- $f(\cdot)$: activation function @ encoder
- $g(\cdot)$: activation function @ decoder
How to Modeling
-
Prediction
\[\begin{aligned} \hat{\mathbf{r}}_{i} &= g\left[\mathbf{W} \cdot f(\mathbf{V} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{r}}_{i} + \overrightarrow{\beta}) + \overrightarrow{\mathbf{b}} \right] \end{aligned}\]-
Encoder(Dimensionality Reduction):
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{i} &= f(\mathbf{V} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{r}}_{i} + \overrightarrow{\beta}) \end{aligned}\] -
Decoder(Reconstruction):
\[\begin{aligned} \hat{\mathbf{r}}_{i} &= g(\mathbf{W} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{i} + \overrightarrow{\mathbf{b}}) \end{aligned}\]
-
-
Optimization
\[\begin{aligned} \hat{\Theta} &= \text{arg} \min{\sum_{i=1}^{N}{\Vert \overrightarrow{\mathbf{r}}_{i} - h(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{r}}_{i} ; \Theta) \Vert_{\mathcal{O}}^{2}} + \frac{\lambda}{2}\Vert \Theta \Vert_{F}^{2}} \end{aligned}\]- \(h(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{r}}_{i} ; \Theta)\): Reconstruction Output
- \(\Theta\): Learning Parameters
- \(\Vert \cdot \Vert_{\mathcal{O}}^{2}\): L2 Loss Computed only for Observed Entries
- \(\Vert \cdot \Vert_{F}^{2}\): Regularization Term
This post is licensed under
CC BY 4.0
by the author.