Convolutional Neural Networks
Based on the following lectures
(1) “Intro. to Deep Learning (2023-2)” by Prof. Seong Man An, Dept. of Data Science, The Grad. School, Kookmin Univ.
(2) “Vision AI (2024-1)” by Prof. Jong Hyuk Park, Dept. of Data Science, The Grad. School, Kookmin Univ.
Why? Conv-Net
-
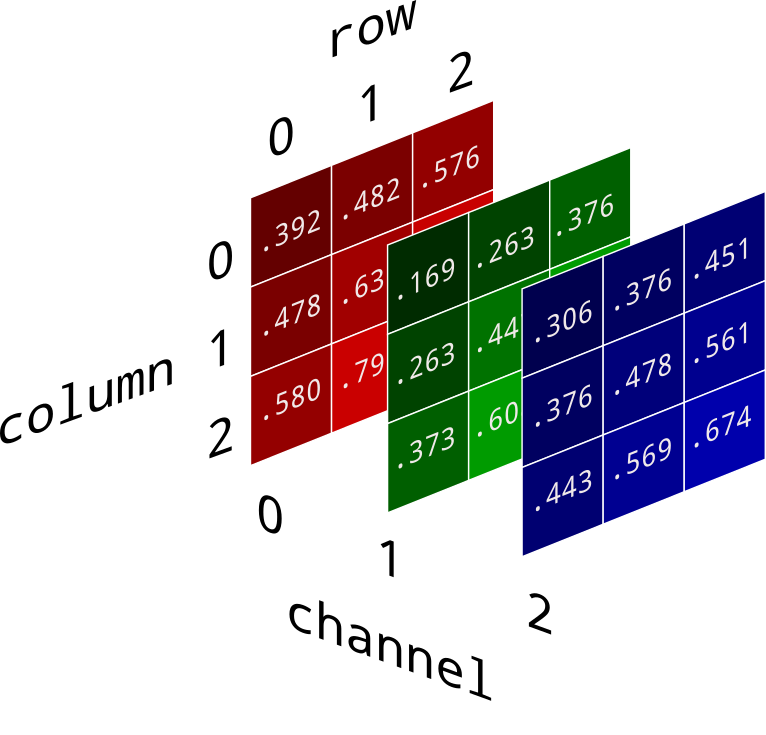
image datais spatially structured data: -
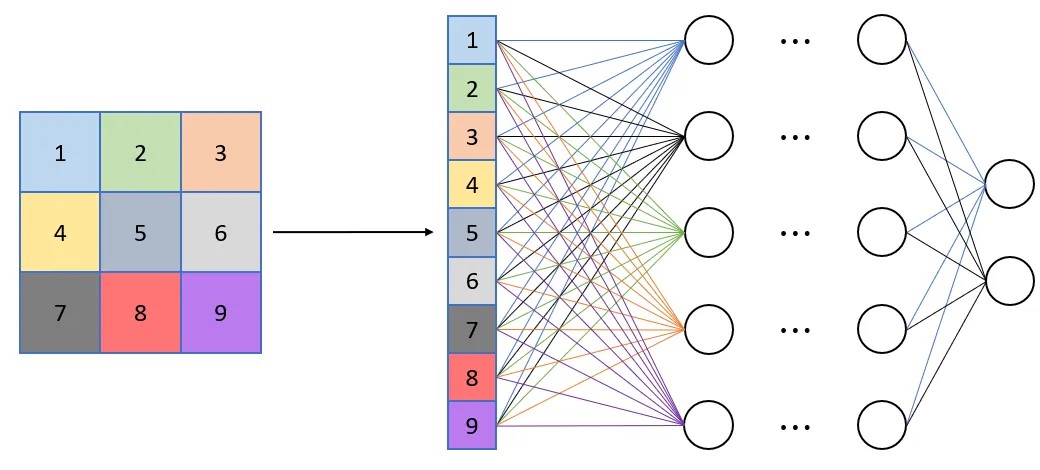
fully connected layersflatten the dimensionality of the input,
collapsing its spatial structure: -
CNN(ConvolutionalNeuralNetworks) involvespreprocessingoperations
that preservespatial structure:
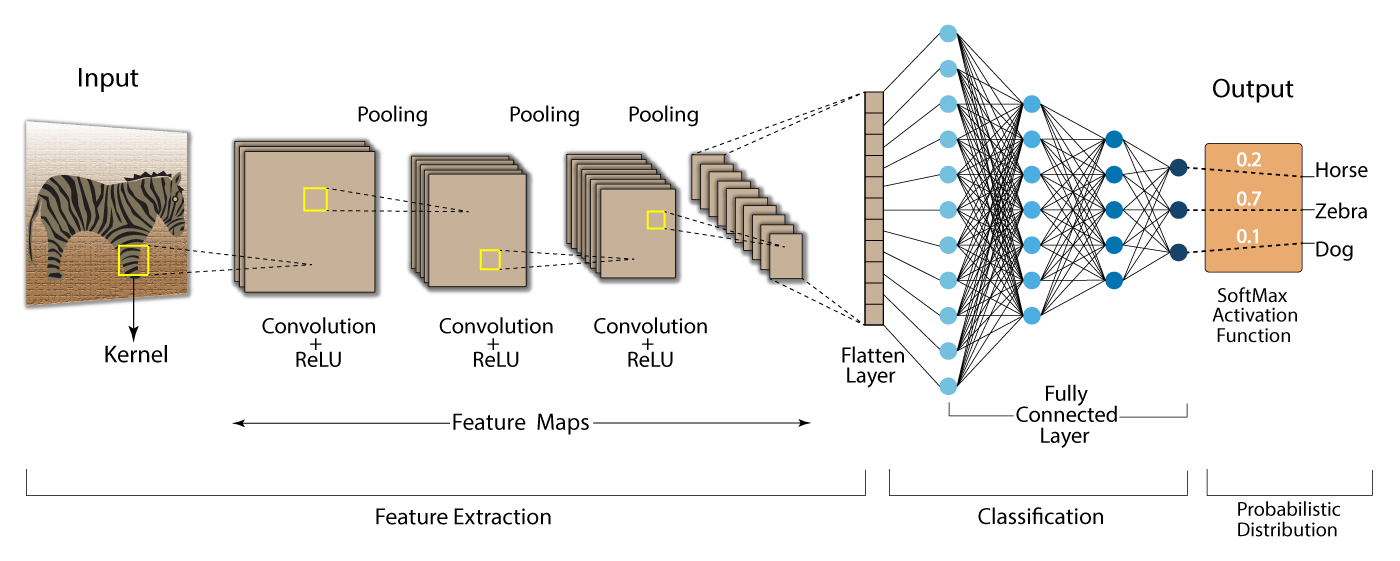
How to Extract Features
-
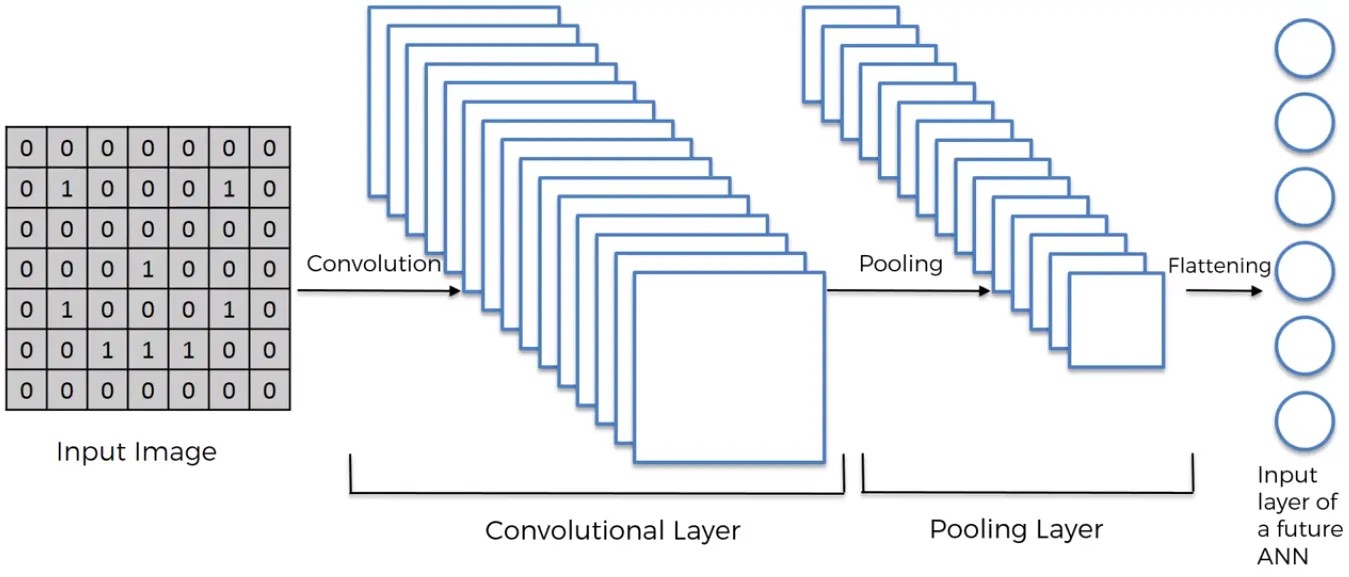
Components
- 합성곱 레이어(Convolution Layer)
- 합동 레이어(Pooling Layer)
- 평탄화 레이어(Flatten Layer)
- 완전 연결 계층(Fully-Connected Layer)
-
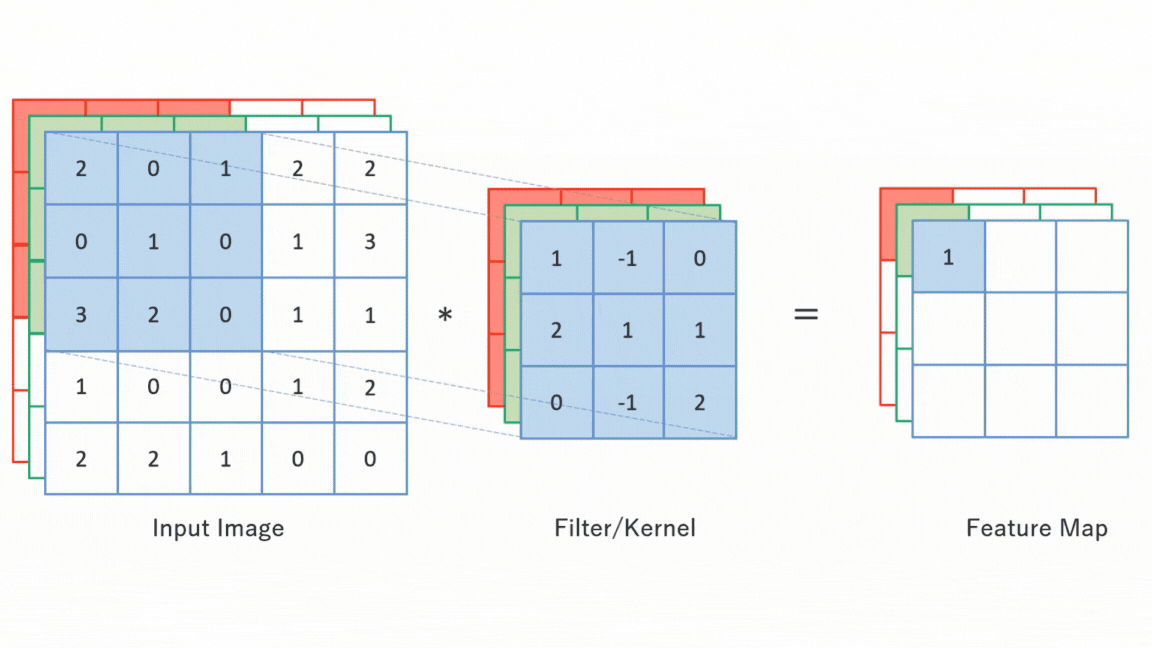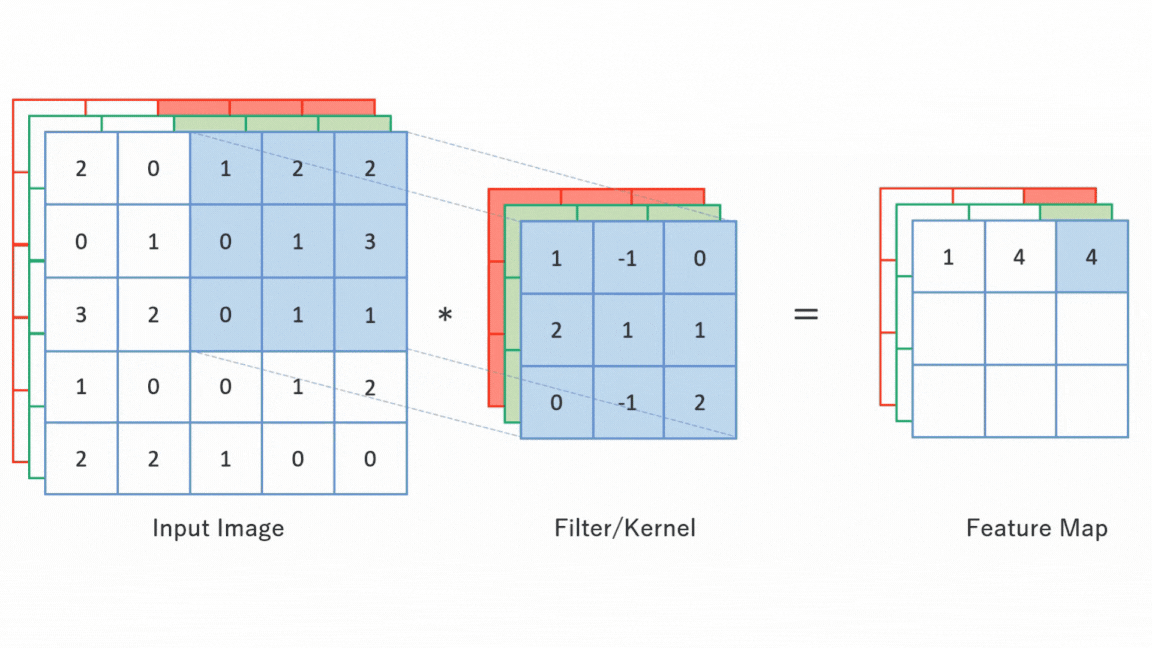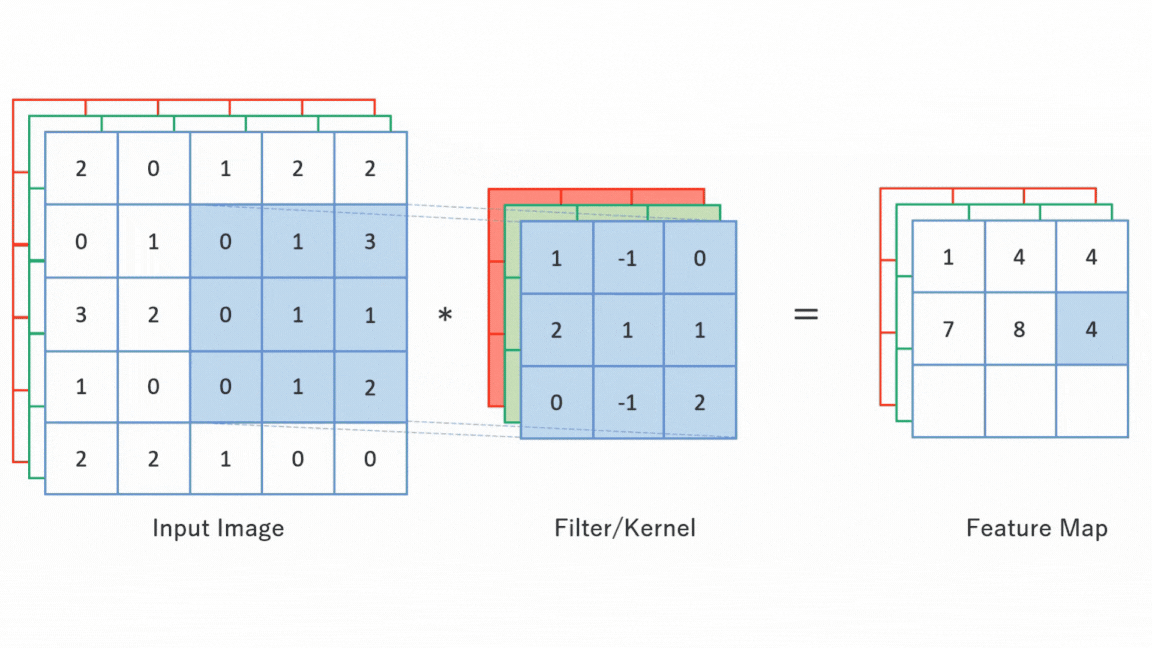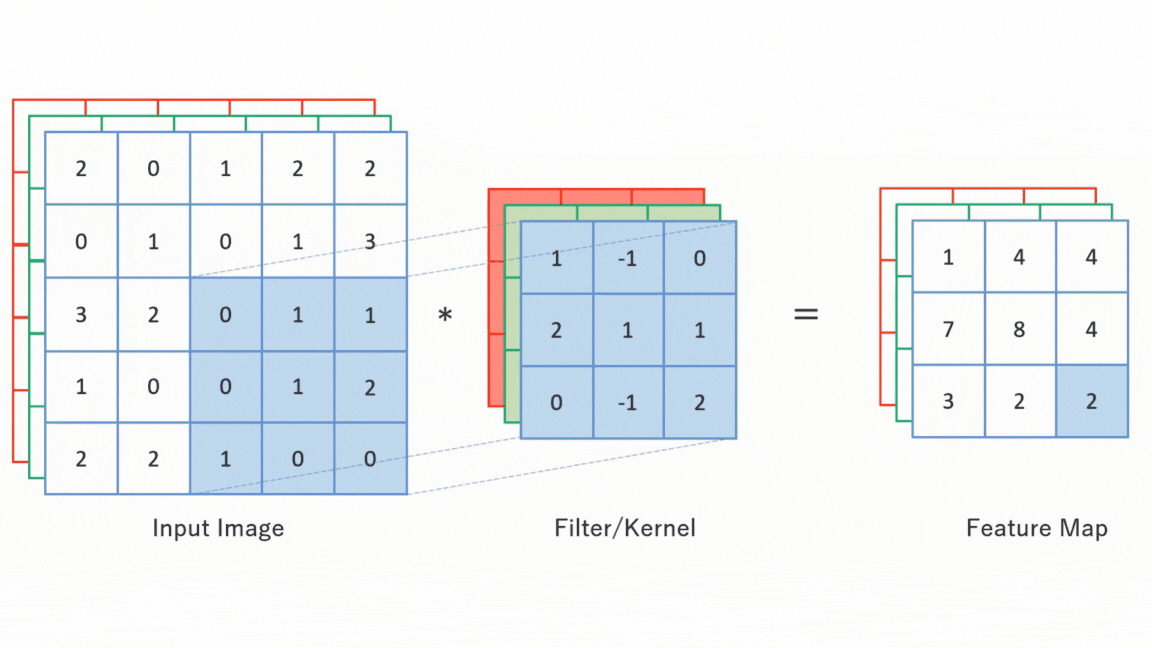
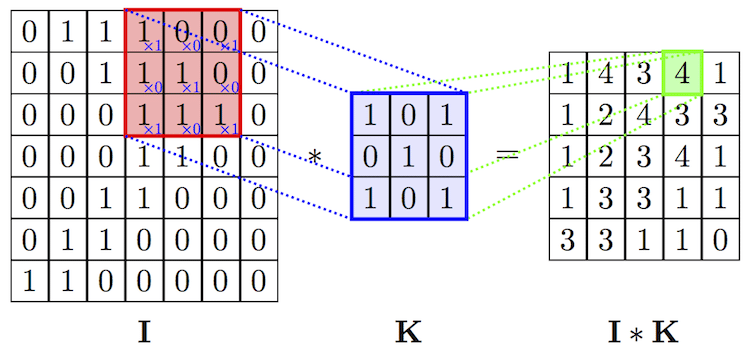
합성곱 연산(Convolution Operation): 입력값의 부분 공간을 커널(Kernel)과 요소별 곱셈(Element-wise Product) 및 그 결과를 합산하여 피처 맵(Feature Map)을 추출하는 연산
-
커널(Kernel): 입력값의 부분 공간과 요소별 곱셈(Element-wise Product)하는 여과기(Filter)
-
피처 맵(Feature Map) : 합성곱 연산 결과 입력값 형상의 특징으로서 반환된 새로운 배열로서 원소값은 부분 공간이 커널과 매칭되는 정도를 나타냄
-
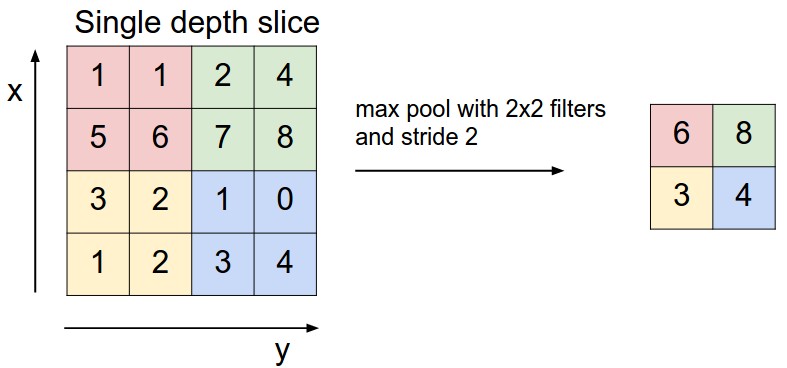
합동 연산(Pooling Operation): 피처 맵(Featur Map)에 대하여 그 부분 공간마다 대표값을 추출하여 요약된 행렬을 구성하는 연산
Sourse
- https://medium.com/@PK_KwanG/cnn-step-2-flattening-50ee0af42e3e
- https://medium.com/@alejandro.itoaramendia/convolutional-neural-networks-cnns-a-complete-guide-a803534a1930