Latent Factor Model with Attention Mechanism
Based on the following lectures
(1) “Recommendation System Design (2024-1)” by Prof. Ha Myung Park, Dept. of Artificial Intelligence. College of SW, Kookmin Univ.
(2) "Recommender System (2024-2)" by Prof. Hyun Sil Moon, Dept. of Data Science, The Grad. School, Kookmin Univ.
DACR: History Embedding with ATTN
- 문제 의식: Implicit Feedback Problem
DeepCF- 표현 학습(Representation Learning): 사용자와 아이템 간 선형 관계를 바탕으로 저차원 잠재요인 공간을 효율적으로 구성
- 매칭 함수 학습(Matching Function Learning): 다양한 매칭 함수를 근사하여 사용자와 아이템 간 비선형 상호작용 포착
- Implicit Feedback Problem
- 관측치의 불완전성(Observation Incompleteness): 관측과 미관측이 반드시 선호와 비선호를 의미하지 않음
- 선호의 비가시성(Hidden Signal): 관측치의 불완전성으로 인하여 선호의 정도나 의도를 포착하기 어려움
- 즉, 암시적 피드백 데이터는 행동 매칭 데이터이기에 선호 매칭에 사용하기 위해서는 내재된 선호 정보를 부각하고 잡음을 여과하는 절차가 필요함
DACR(DeepCollaborativeRecommendation Algorithm Based onAttention Mechanism): 사용자, 아이템 표현 및 그 결합 표현에 어텐션 메커니즘(Attention Mechanism)을 적용하여 차원별 가중치를 명시적으로 설계함으로써 입력 중 집중할(Focus) 정보를 선별하여 강조하는 앙상블 모형- Cui, C., Qin, J., & Ren, Q.
(2022).
Deep collaborative recommendation algorithm based on attention mechanism.
Applied Sciences, 12(20), 10594.
- Cui, C., Qin, J., & Ren, Q.
- Components
ARL:AttentionRepresentationLearningAML:AttnetionMatching FunctionLearningDACR:ARL&AMLEmsemble
Notation
- $u=1,2,\cdots,M$: user idx
- $i=1,2,\cdots,N$: item idx
- $\mathbf{Y} \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times N}$: user-item interaction matrix
- $\overrightarrow{\mathbf{u}}_{u} \in \mathbb{R}^{K}$: user latent factor vector
- $\overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}_{i} \in \mathbb{R}^{K}$: item latent factor vector
- $\overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i}$: predictive vector of user $u$ and item $i$
- $\hat{y}_{u,i}$: interaction probability of user $u$ and item $i$
- $\delta$: softmax function
- $\sigma$: sigmoid function
How to Modeling
-
\[\begin{aligned} \hat{y}_{u,i} &= \sigma(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{w}} \cdot [\overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i}^{\text{(ARL)}} \oplus \overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i}^{\text{(AML)}}]) \end{aligned}\]DACRisARL&AMLEmsemble
ARL
-
Linear Transformation:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{p}}_{u} &= \mathbf{W} \cdot \mathbf{Y}_{u*}\\ \overrightarrow{\mathbf{q}}_{i} &= \mathbf{W} \cdot \mathbf{Y}_{*i} \end{aligned}\]- $\overrightarrow{\mathbf{p}}_{u} \in \mathbb{R}^{D}$
- $\overrightarrow{\mathbf{q}}_{i} \in \mathbb{R}^{D}$
-
Attention Weight:
\[\begin{aligned} \alpha_{u} &= \delta(\mathbf{W} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{p}}_{u} + \overrightarrow{\mathbf{b}})\\ \alpha_{i} &= \delta(\mathbf{W} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{q}}_{i} + \overrightarrow{\mathbf{b}}) \end{aligned}\] -
Representation Learning:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{u}}_{u} &= \text{MLP}_{\text{ReLU}}\left(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{p}}_{u} \oplus [\alpha_{u} \odot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{p}}_{u}]\right)\\ \overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}_{i} &= \text{MLP}_{\text{ReLU}}\left(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{q}}_{i} \oplus [\alpha_{i} \odot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{q}}_{i}]\right) \end{aligned}\] -
predictive vector of user $u$ and item $i$:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i} &= \overrightarrow{\mathbf{u}}_{u} \odot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}_{i} \end{aligned}\] -
if use
\[\begin{aligned} \hat{y}_{u,i} &= \sigma(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{w}} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i}) \end{aligned}\]ARLas a single prediction module:
AML
-
History Embedding:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{u}}_{u} &= \mathbf{W} \cdot \mathbf{Y}_{u*}\\ \overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}_{i} &= \mathbf{W} \cdot \mathbf{Y}_{*i} \end{aligned}\] -
Vector Concatenation:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{x}}_{u,i} &= \overrightarrow{\mathbf{p}}_{u} \oplus \overrightarrow{\mathbf{q}}_{i} \end{aligned}\] -
Attention Weight:
\[\begin{aligned} \alpha_{u,i} &= \delta(\mathbf{W} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{x}}_{u,i} + \overrightarrow{\mathbf{b}}) \end{aligned}\] -
Matching Function Learning:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i} &= \text{MLP}_{\text{ReLU}}\left(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{x}}_{u,i} \oplus [\alpha_{u,i} \odot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{x}}_{u,i}]\right) \end{aligned}\] -
if use
\[\begin{aligned} \hat{y}_{u,i} &= \sigma(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{w}} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i}) \end{aligned}\]AMLas a single prediction module:
DRNet: Aggregate User’s Histories
- 문제 의식
- 기존 협업 필터링이 모델링하는 관계 유형
- 잠재요인 모형(Latent Factor Model): 사용자-아이템 관계 모델링, 개인화 추천 성능 우수 (ex.
NCF) - 아이템 기반 협업 필터링(User Free Model): 아이템-아이템 관계 모델링, 데이터 희소성 강건 (ex.
SLIM,FISM)
- 잠재요인 모형(Latent Factor Model): 사용자-아이템 관계 모델링, 개인화 추천 성능 우수 (ex.
- 어텐션 기반 히스토리 아이템 집계 방식 (ex.
NAIS)- 사용자가 과거에 더 선호한 아이템일수록 새로운 아이템 선택에 더 큰 영향력을 행사함
- 사용자의 선호 정도에 기반하여 집중도를 차등 부여하여 집계할 필요가 있음
- 기존 협업 필터링이 모델링하는 관계 유형
DRNet(DualRelationNet-work) : 사용자-아이템 매칭 함수와 아이템-아이템 매칭 함수를 병렬 학습하는 모형- Ji, D., Xiang, Z., & Li, Y.
(2020).
Dual relations network for collaborative filtering.
IEEE Access, 8, 109747-109757.
- Ji, D., Xiang, Z., & Li, Y.
- Components
- Affection Network: Modeling User-Item Relation
- Association Network: Modeling Item-Item Relation
- Dual-Relation Network: Affection Network & Association Network Combination
Notation
- $u=1,2,\cdots,M$: user idx
- $i=1,2,\cdots,N$: item idx
- $\mathbf{Y} \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times N}$: user-item interaction matrix
- $\overrightarrow{\mathbf{u}}_{u} \in \mathbb{R}^{K}$: user id embedding vector @ affection network
- $\overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}_{i} \in \mathbb{R}^{K}$: item id embedding vector @ affection network
- $\overrightarrow{\mathbf{p}}_{i} \in \mathbb{R}^{K}$: target item id embedding vector @ association network
- $\overrightarrow{\mathbf{q}}_{j} \in \mathbb{R}^{K}$: history item id embedding vector @ association network
- $\overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i}$: predictive vector of user $u$ and item $i$
- $\hat{y}_{u,i}$: interaction probability of user $u$ and item $i$
How to Modeling
-
Dual-Relation Network:
\[\begin{aligned} \hat{y}_{u,i} &= \sigma\left(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{w}} \cdot [\overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i}^{\text{(AFFECT)}} \oplus \overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i}^{\text{(ASSO)}}]\right) \end{aligned}\]
Affection Network
-
ID Embedding:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{u}}_{u} &= \text{Emb}(u)\\ \overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}_{i} &= \text{Emb}(i) \end{aligned}\] -
Predictive Vector of user $u$ and item $i$:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i} &= \text{MLP}_{\text{ReLU}}(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{u}}_{u} \odot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}_{i}) \end{aligned}\]
Association Network
-
ID Embedding:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{p}}_{i} &= \text{Emb}(i)\\ \overrightarrow{\mathbf{q}}_{j} &= \text{Emb}(j) \end{aligned}\] -
Global Item Vector of User $u$:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{x}}_{u} &= \text{ATTN}(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}},\text{Affection}(u,\forall j \in \mathcal{R}_{u}^{+} \setminus \{i\}), \mathbf{Q}[\forall j \in \mathcal{R}_{u}^{+} \setminus \{i\},:]) \end{aligned}\] -
Predictive Vector of user $u$ and item $i$:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i} &= \text{MLP}_{\text{ReLU}}(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{x}}_{u} \odot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{p}}_{i}) \end{aligned}\]
How to Attention
-
Query Vector is Global Context Vector:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}} \end{aligned}\] -
Key Vector is Generated by Affection Network:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i}^{\text{(AFFECT)}} &= \text{MLP}_{\text{ReLU}}(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{u}}_{u} \odot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{v}}_{i}) \end{aligned}\] -
Global Item Vector of User $u$ is Generated by:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{x}}_{u} &= \sum_{j \in \mathcal{R}_{u}^{+} \setminus \{i\}}{\alpha_{u,j} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{q}}_{j}} \end{aligned}\] -
Attention Weight is Calculated by Smoothed Softmax:
\[\begin{aligned} \alpha_{u,j} &= \frac{\exp{f(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}},\overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,j}^{\text{(AFFECT)}})}}{\left[\sum_{j \in \mathcal{R}_{u}^{+} \setminus \{i\}}{\exp{f(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}},\overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,j}^{\text{(AFFECT)}})}}\right]^{\beta}} \end{aligned}\]- $0 < \beta \le 1$: Smoothing Factor
-
Attention Score Function is Dot Product:
\[\begin{aligned} f(q,k) &= q \cdot k \end{aligned}\]
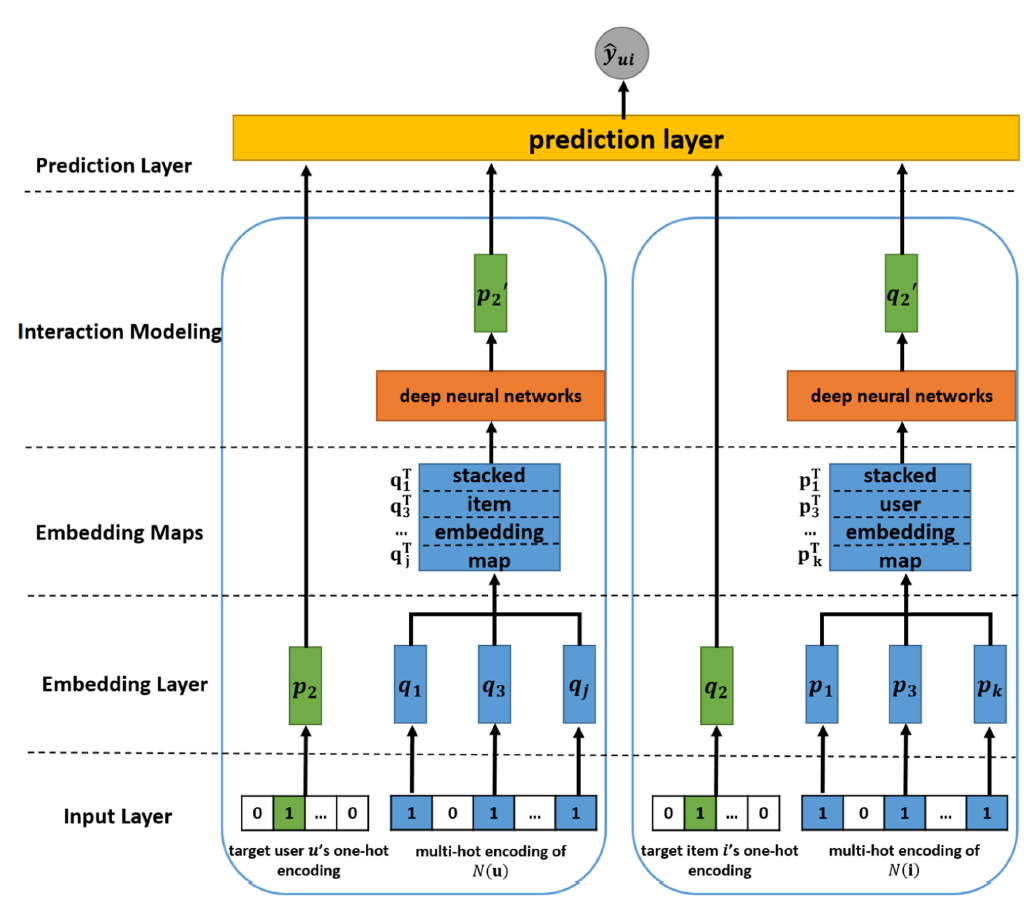
DELF: Aggregate User & Item’s Histories
- 문제 의식: 아이디 임베딩(ID Embedding)과 히스토리 임베딩(History Embedding)의 상호 보완적 관계
- 아이디 임베딩은 고유 정보를 보존한 표현을 생성하는 데 강점
- 히스토리 임베딩은 맥락 정보를 반영한 표현을 생성하는 데 강점
DELF(DualEmbedding based DeepLatentFactor Model): 사용자와 아이템의 아이디 임베딩과 히스토리 임베딩을 조합하여 다양한 매칭 함수를 병렬 학습하는 모형- Cheng, W., Shen, Y., Zhu, Y., & Huang, L.
(2018, July).
DELF: A dual-embedding based deep latent factor model for recommendation.
In IJCAI (Vol. 18, pp. 3329-3335).
- Cheng, W., Shen, Y., Zhu, Y., & Huang, L.
Notation
- $u=1,2,\cdots,M$: user idx
- $i=1,2,\cdots,N$: item idx
- $\mathbf{R} \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times N}$: user-item interaction matrix
- $\overrightarrow{\mathbf{p}}_{u} \in \mathbb{R}^{K}$: user ID embedding vector
- $\overrightarrow{\mathbf{q}}_{i} \in \mathbb{R}^{K}$: item ID embedding vector
- $\overrightarrow{\mathbf{m}}_{u} \in \mathbb{R}^{K}$: user history embedding vector
- $\overrightarrow{\mathbf{n}}_{i} \in \mathbb{R}^{K}$: item history embedding vector
- $\overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i}$: predictive vector of user $u$ and item $i$
- $\hat{y}_{u,i}$: interaction probability of user $u$ and item $i$
How to Modeling
-
ID Embedding:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{p}}_{u} &=\text{Emb}(u)\\ \overrightarrow{\mathbf{q}}_{i} &=\text{Emb}(i) \end{aligned}\] -
History Embedding:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{m}}_{u} &=\text{ATTN}(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}}^{\text{(user)}}, \mathbf{H}[\forall j \in \mathcal{R}_{u}^{+} \setminus \{i\},:], \mathbf{Y}[\forall j \in \mathcal{R}_{u}^{+} \setminus \{i\},:])\\ \overrightarrow{\mathbf{n}}_{i} &=\text{ATTN}(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}}^{\text{(item)}}, \mathbf{H}[\forall v \in \mathcal{R}_{i}^{+} \setminus \{u\},:], \mathbf{X}[\forall v \in \mathcal{R}_{i}^{+} \setminus \{u\},:]) \end{aligned}\] -
Pairwise Neural Interaction Layers:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i}^{(1)} &= \text{MLP}_{\text{ReLU}}(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{p}}_{u} \oplus \overrightarrow{\mathbf{q}}_{i})\\ \overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i}^{(2)} &= \text{MLP}_{\text{ReLU}}(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{m}}_{u} \oplus \overrightarrow{\mathbf{n}}_{i})\\ \overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i}^{(3)} &= \text{MLP}_{\text{ReLU}}(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{p}}_{u} \oplus \overrightarrow{\mathbf{n}}_{i})\\ \overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i}^{(4)} &= \text{MLP}_{\text{ReLU}}(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{m}}_{u} \oplus \overrightarrow{\mathbf{q}}_{i}) \end{aligned}\] -
Predict interaction probability of user $u$ and item $i$:
\[\begin{aligned} \hat{y}_{u,i} &= \sigma(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{w}} \cdot [\overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i}^{(1)} \oplus \overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i}^{(2)} \oplus \overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i}^{(3)} \oplus \overrightarrow{\mathbf{z}}_{u,i}^{(4)}] + \overrightarrow{\mathbf{b}}) \end{aligned}\]
How to Attention
-
Another ID Embedding:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{x}}_{v} &=\text{Emb}(v)\\ \overrightarrow{\mathbf{y}}_{j} &=\text{Emb}(j) \end{aligned}\] -
Query Vector is Global Context Vector:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}}^{\text{(user)}}, \quad \overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}}^{\text{(item)}} \end{aligned}\] -
Key Vector is Generated by:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}}_{v} &= \text{tanh}(\mathbf{W} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{x}}_{v} + \overrightarrow{\mathbf{b}})\\ \overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}}_{j} &= \text{tanh}(\mathbf{W} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{y}}_{j} + \overrightarrow{\mathbf{b}}) \end{aligned}\] -
History Embedding Vector is Generated by:
\[\begin{aligned} \overrightarrow{\mathbf{m}}_{u} &= \sum_{j \in \mathcal{R}_{u}^{+} \setminus \{i\}}{\alpha_{j} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{y}}_{j}}\\ \overrightarrow{\mathbf{n}}_{i} &= \sum_{v \in \mathcal{R}_{i}^{+} \setminus \{u\}}{\alpha_{v} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathbf{x}}_{v}}\\ \end{aligned}\] -
Attention Weight is Calculated by Softmax:
\[\begin{aligned} \alpha_{j} &= \frac{\exp{f(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}}^{\text{(user)}},\overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}}_{j})}}{\sum_{j \in \mathcal{R}_{u}^{+} \setminus \{i\}}{\exp{f(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}}^{\text{(user)}},\overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}}_{j})}}}\\ \alpha_{v} &= \frac{\exp{f(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}}^{\text{(item)}},\overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}}_{v})}}{\sum_{v \in \mathcal{R}_{i}^{+} \setminus \{u\}}{\exp{f(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}}^{\text{(item)}},\overrightarrow{\mathbf{h}}_{v})}}} \end{aligned}\] -
Attention Score Function is Dot Product:
\[\begin{aligned} f(q,k) &= q \cdot k \end{aligned}\]