Language Model
Based on the lecture “Text Analytics (2024-1)” by Prof. Je Hyuk Lee, Dept. of Data Science, The Grad. School, Kookmin Univ.
Language Model
- 언어 모형(Language Model) : Word Sequence(문장)에 확률을 할당하여 가장 자연스러운 문장을 탐색하는 모형
Statistical Language Model
SLM
-
SLM(
\[\begin{aligned} P(W) &= P(w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_n)\\ &= \cancel{P(w_1)} \cdot \frac{\cancel{P(w_1,w_2)}}{\cancel{P(w_1)}} \cdot \frac{\cancel{P(w_1, w_2, w_3)}}{\cancel{P(w_1, w_2)}} \cdots \frac{P(w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_n)}{\cancel{P(w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_{n-1})}}\\ &= P(w_1) \cdot P(w_2 \mid w_1) \cdot P(w_3 \mid w_1, w_2) \cdots P(w_n \mid w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_{n-1})\\ &= \prod_{i=1}^{n}{P(w_i \mid w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_{i-1})} \end{aligned}\]StatisticalLanguageModel) : 조건부 확률을 활용하여 Word Sequence 발생 확률을 부여하는 모형 -
확률 부여 방법
\[\begin{aligned} P(w_i \mid w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_{i-1}) &= \frac{\text{Count}(w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_i)}{\text{Count}(w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_{i-1})} \end{aligned}\]- $\text{Count}(w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_i)$ : 말뭉치에서 Word Sequence $(w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_i)$ 가 등장한 횟수
n-Gram
-
n-Gram : $i$ 번째 단어를 예측함에 있어 $N-1$ 개의 단어만을 활용하는 방법
\[\begin{aligned} P(W) &= \prod_{i=1}^{n}{P(w_{i} \mid w_{i-(n-1)}, w_{i-(n-2)}, \cdots, w_{i-1})} \end{aligned}\] -
How to Select $n$ : 통상 $n \le 5$ 권장
Problem Small $n$ Large $n$ Sparsity Problem $\downarrow$ $\uparrow$ Long-term Dependency $\uparrow$ $\downarrow$ - 희소성 문제(Sparsity Problem) : 충분한 데이터를 관측하지 못하여 언어를 정확히 모델링하지 못하는 문제
- 장기 의존성 문제(Long-term Dependency) : 문맥 내에서 멀리 떨어져 있는 단어들 간의 관계를 처리하는 문제
Neural Networks based Langauge Model
- 통계적 방법론의 한계점과 그 대안
- NNLM(
NeuralNetworksLangaugeModel) : 임베딩을 활용한 희소성 문제 보완 - RNNLM(
RecurrentNeuralNetworksLangaugeModel) : RNN 계열 레이어를 활용한 장기 의존성 문제 보완
- NNLM(
-
How to Generate a Context Vector for $w_{t+1}$
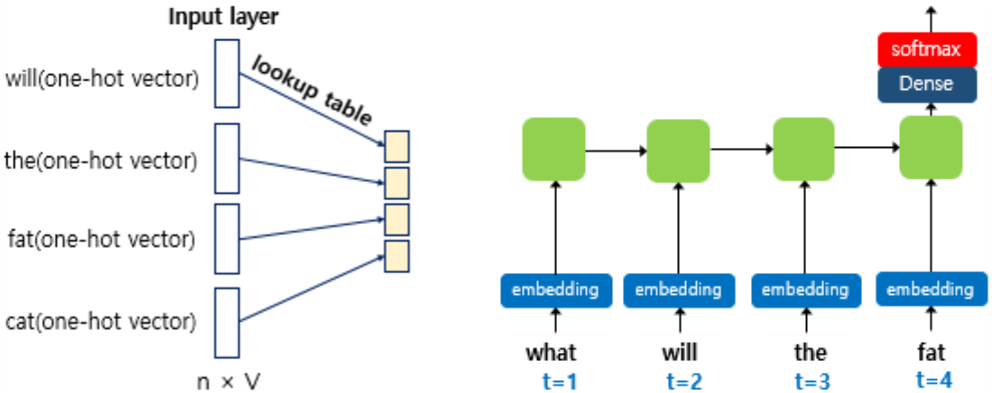
- NNLM : $t$ 번째까지 등장한 단어 벡터들의 결합(Concatenation)으로 생성
- RNNLM : $t$ 번째까지 등장한 단어 벡터들을 RNN 계열 레이어에 순차 입력하여 생성
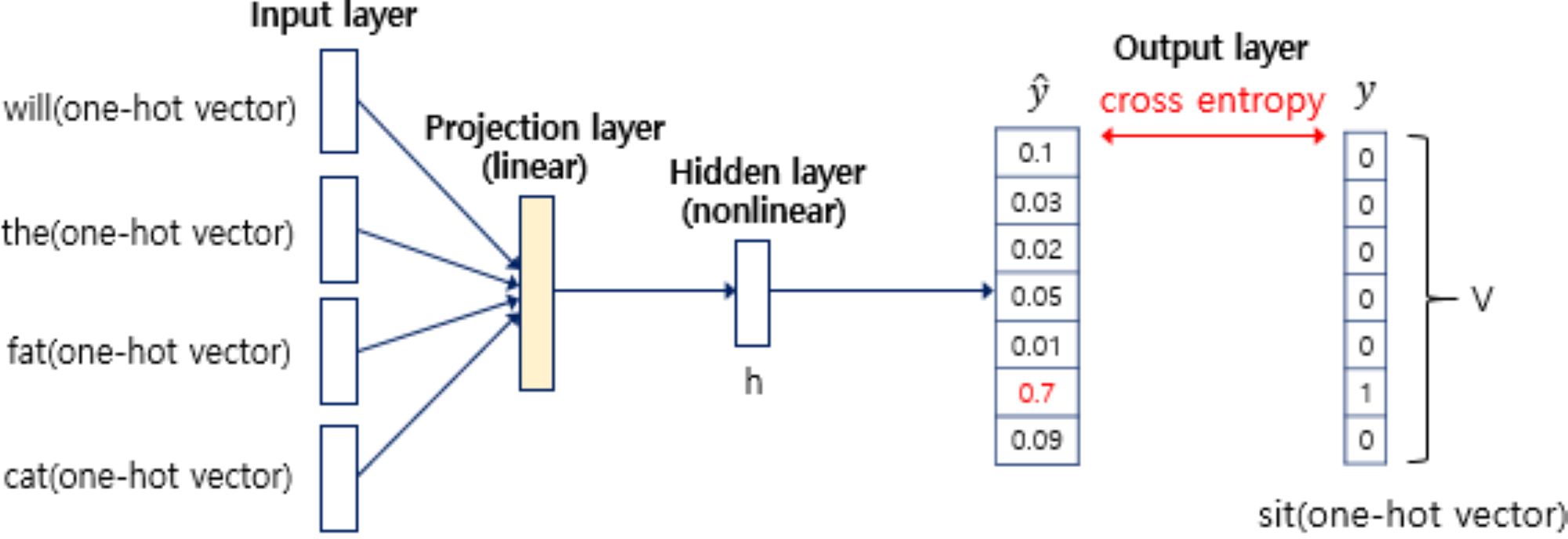
NNLM
INPUT→PROJECTION- Projection : \(\mathbf{w}_{i} = \mathbf{x}_{i} \cdot \mathbf{W}\)
- Concatenation : \(\mathbf{z}_{t} = \mathbf{w}_{t-n+1} \oplus \mathbf{w}_{t-n+2} \oplus \cdots \oplus \mathbf{w}_{t}\)
-
\[\begin{aligned} \mathbf{h}_{t} &= \text{F}_{\text{ReLU}}\left[\mathbf{z}_{t}\right] \end{aligned}\]PRJECTION→HIDDEN -
\[\begin{aligned} \hat{\mathbf{y}}_{t+1} &= \text{F}_{\text{Softmax}}\left[\mathbf{h}_{t}\right] \end{aligned}\]HIDDEN→OUTPUT
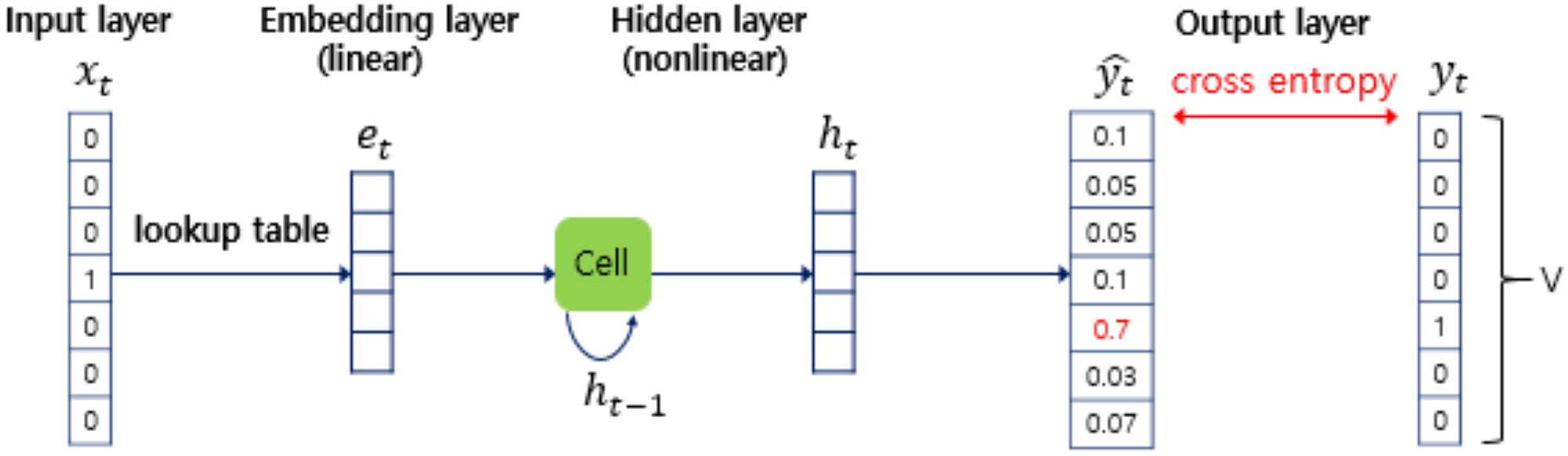
RNNLM
-
\[\mathbf{w}_{i} = \mathbf{x}_{i} \cdot \mathbf{W}\]INPUT→PROJECTION -
\[\begin{aligned} h_{t}, c_{t} &= \text{LSTM}\left(\mathbf{w}_{t}, h_{t-1}, c_{t-1}\right) \end{aligned}\]PRJECTION→HIDDEN -
\[\begin{aligned} \hat{\mathbf{y}}_{t+1} &= \text{F}_{\text{Softmax}}\left[h_{t}\right] \end{aligned}\]HIDDEN→OUTPUT
Metric
-
PPL(
\[\begin{aligned} PPL(W) &= P(W)^{-\frac{1}{N}}\\ &= P(w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_N)^{-\frac{1}{N}}\\ &= \sqrt[N]{\frac{1}{P(w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_N)}}\\ &= \sqrt[N]{\frac{1}{\prod_{i=1}^{n}{P(w_N \mid w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_{N-1})}}} \end{aligned}\]PerPLexity) : 언어 모형의 성능 평가 지표 -
해석 : 선택 가능한 경우의 수를 의미하는 분기 계수(Branching Factor)로서, 특정 시점마다 평균적으로 고민하는 선택지 수
\[\begin{aligned} PPL(W) &=10\\ \sqrt[N]{\frac{1}{\prod_{i=1}^{n}{P(w_N \mid w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_{N-1})}}} &= 10\\ \prod_{i=1}^{n}{P(w_N \mid w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_{N-1})} &= \left(\frac{1}{10}\right)^{N}\\ \underset{\frac{1}{10}}{P(w_1)} \cdot \underset{\frac{1}{10}}{P(w_2 \mid w_1)} \cdot \underset{\frac{1}{10}}{P(w_3 \mid w_1, w_2)} \cdots \underset{\frac{1}{10}}{P(w_N \mid w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_{N-1})} &= \left(\frac{1}{10}\right)^{N} \end{aligned}\]
This post is licensed under
CC BY 4.0
by the author.