Monte Carlo Simulation
Based on the lecture “Bayesian Modeling (2024-1)” by Prof. Yeo Jin Chung, Dept. of AI, Big Data & Management, College of Business Administration, Kookmin Univ.
Monte Carlo Simulation
- 몬테-카를로 시뮬레이션(Monte-Carlo Simulation): 복잡한 시스템이나 수학적 문제의 결과를 예측하기 위해 확률적 샘플링을 사용하는 방법
example $\Pi$
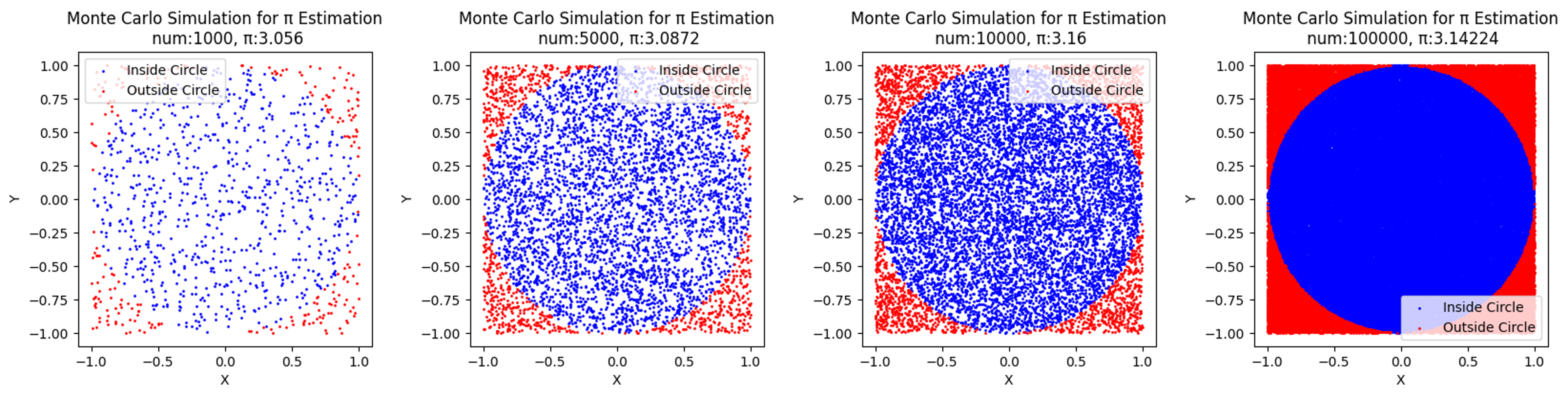
한 변의 길이가 2인 정사각형 내부에 점을 무작위로 찍었을 때, 그 점이 정사각형에 내접하는 원의 내부에 위치할 확률 실험을 전개하여, 원주율 $\pi$ 를 추론하시오.
- 좌표평면 상에서 주어진 조건을 만족하는 원:
정의\(C = \{ (x, y) \mid x^2 + y^2 = r^2 \}\)면적$\pi r^2 = \pi \quad (\because 2r=2)$
- 좌표평면 상에서 주어진 조건을 만족하는 정사각형:
정의\(R = \{ (x, y) \mid -1 \le x \le 1, -1 \le y \le 1\}\)면적$(2r)^2=4$
-
정사각형 내부에 점을 무작위로 찍었을 때, 점이 원 내부에 위치할 가능성:
\[\begin{aligned} P((x,y) \in C) &=\frac{N_{circle}}{N} =\displaystyle\frac{\pi r^2}{(2r)^2} \end{aligned}\]- $N$ : 실행 횟수
- $N_{circle}$ : 성공 횟수(원 내부에 위치한 횟수)
-
몬테-카를로 시뮬레이션을 통한 $\pi$ 추론값 도출:
- 실행 횟수(num)가 증가할수록 $\pi$ 의 추론값이 $3.141592\cdots$ 에 근접해감
Rejection Sampling
-
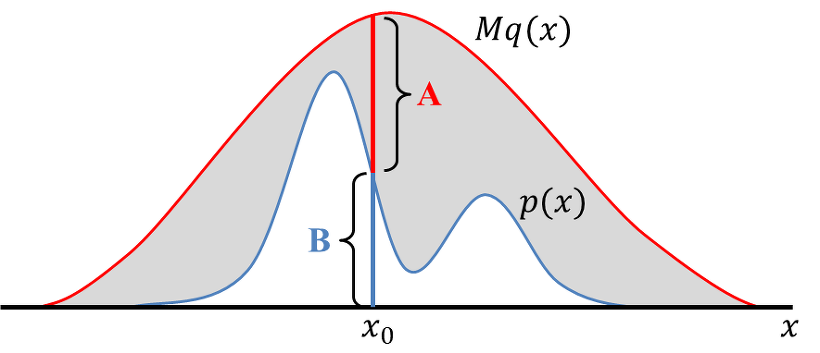
기각 샘플링(Rejection Sampling) : 제안 분포로부터 추출한 관측치를 기각하는 과정을 반복하여 제안 분포를 목표 분포와 유사한 형태로 만드는 방법
-
Target Dist.:
\[\begin{aligned} p(\theta \mid \mathcal{D}) \propto p(\mathcal{D} \mid \theta) \cdot p(\theta) \end{aligned}\] -
Proposed Dist.:
\[\begin{aligned} q(\theta) \end{aligned}\]- $q(\theta)$ must be similar in location and distribution to $p(\theta \mid \mathcal{D})$
- $p(\theta \mid \mathcal{D}) \le M \cdot q(\theta) \quad \text{for} \quad \forall \theta$
-
Rejection Rule:
\[\begin{aligned} \text{Accept} \quad \phi \quad \text{if} \quad u \le \frac{p(\phi \mid \mathcal{D})}{M \cdot q(\phi)} \quad \text{where} \quad u \sim \text{Uniform}(0,1) \end{aligned}\]
This post is licensed under
CC BY 4.0
by the author.