Recurrent Neural Networks
Based on the following lectures
(1) “Intro. to Deep Learning (2023-2)” by Prof. Seong Man An, Dept. of Data Science, The Grad. School, Kookmin Univ.
(2) “Text Analytics (2024-1)” by Prof. Je Hyuk Lee, Dept. of Data Science, The Grad. School, Kookmin Univ.
Why? Recurrent-Net
-
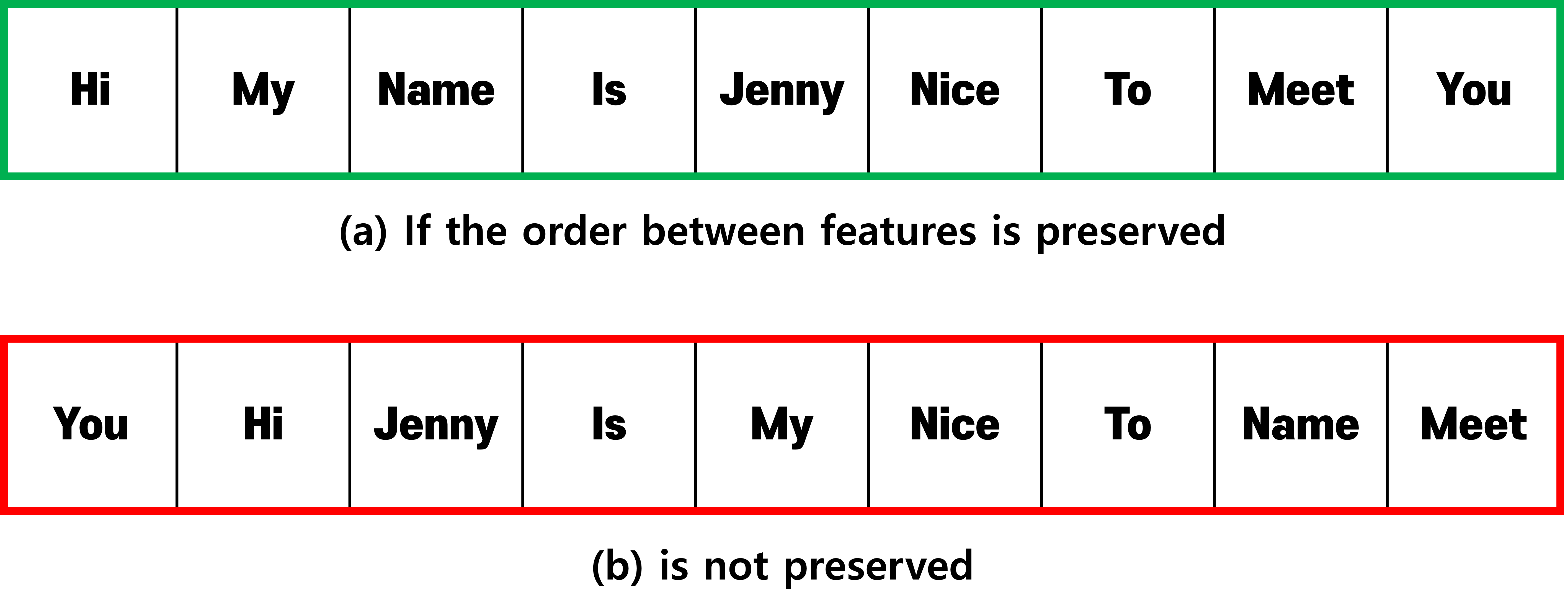
Time series data is data
where there is asequence between features: -
Fully connected layerstreat the positions of input features equally,
so they do not structurally reflectorder informationbetween features: -
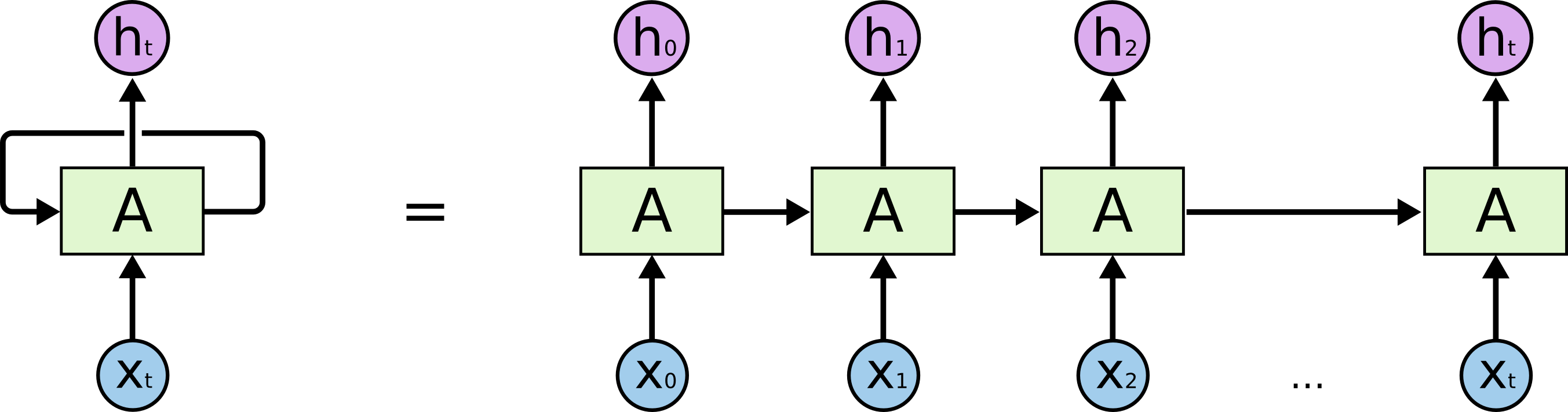
RNN(
RecurrentNeuralNetworks) involvespreprocessingoperations
that preservesequence information:
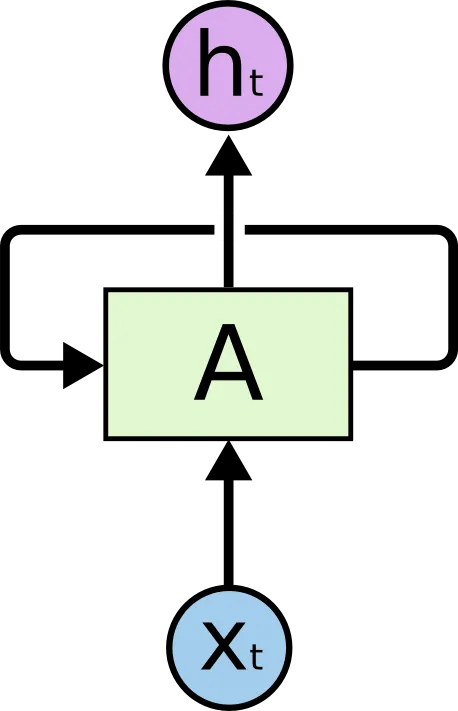
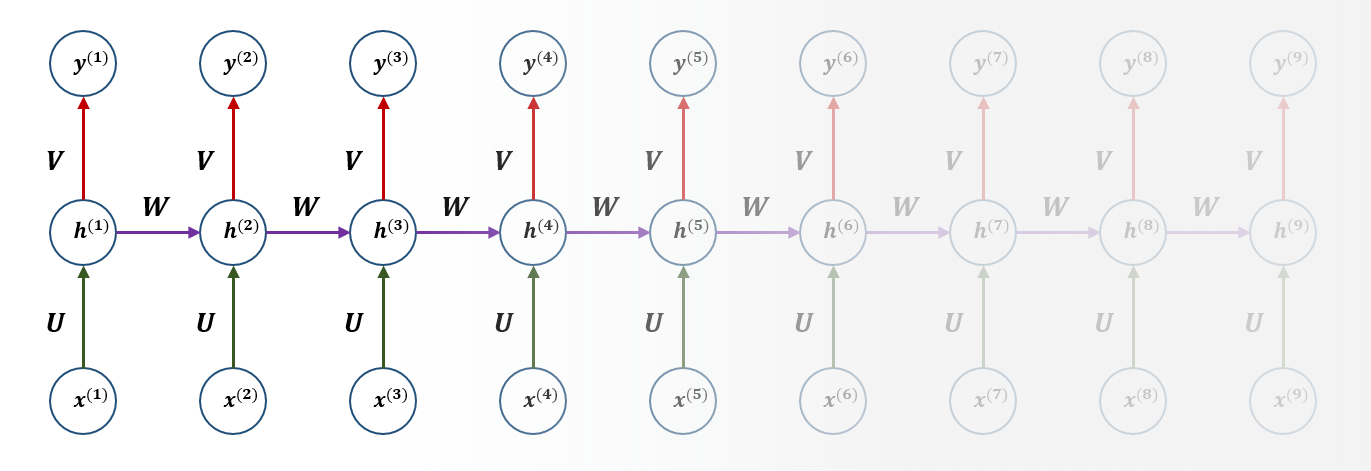
Vanilla RNN
-
update hidden state $\mathbf{z}_{t}$:
\[\begin{aligned} \mathbf{z}_{t} &= \text{tanh}(\mathbf{U}\cdot\mathbf{x}_{t}+\mathbf{W}\cdot\mathbf{z}_{t-1}+\mathbf{b}_{h}) \end{aligned}\]- $\text{tanh}$ : activation function
- $\mathbf{x}_{t}$ : input value @ $t$
- $\mathbf{U}$ : weight matrix of input value @ $t$
- $\mathbf{z}_{t-1}$ : hidden state @ $t-1$
- $\mathbf{W}$ : weight matrix of hidden state @ $t-1$
- $\mathbf{b}_{h}$ : bias
-
print output $\mathbf{y}_{t}$
\[\begin{aligned} \mathbf{y}_{t} &= \text{softmax}(\mathbf{V}\cdot\mathbf{z}_{t}+\mathbf{b}_{o}) \end{aligned}\]- $\text{softmax}$ : activation function
- $\mathbf{z}_{t}$ : hidden state @ $t$
- $\mathbf{V}$ : weight matrix of hidden state @ $t$
- $\mathbf{b}_{o}$ : bias
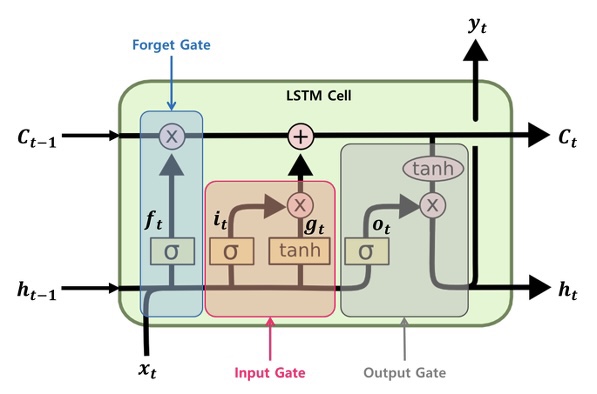
LSTM
-
vanilla rnn suffers from the problems of
long-term dependencies:Long-term dependenciesare problems in which theinitial order informationis not preserved as the sequence gets longer due to thevanishing gradient.
-
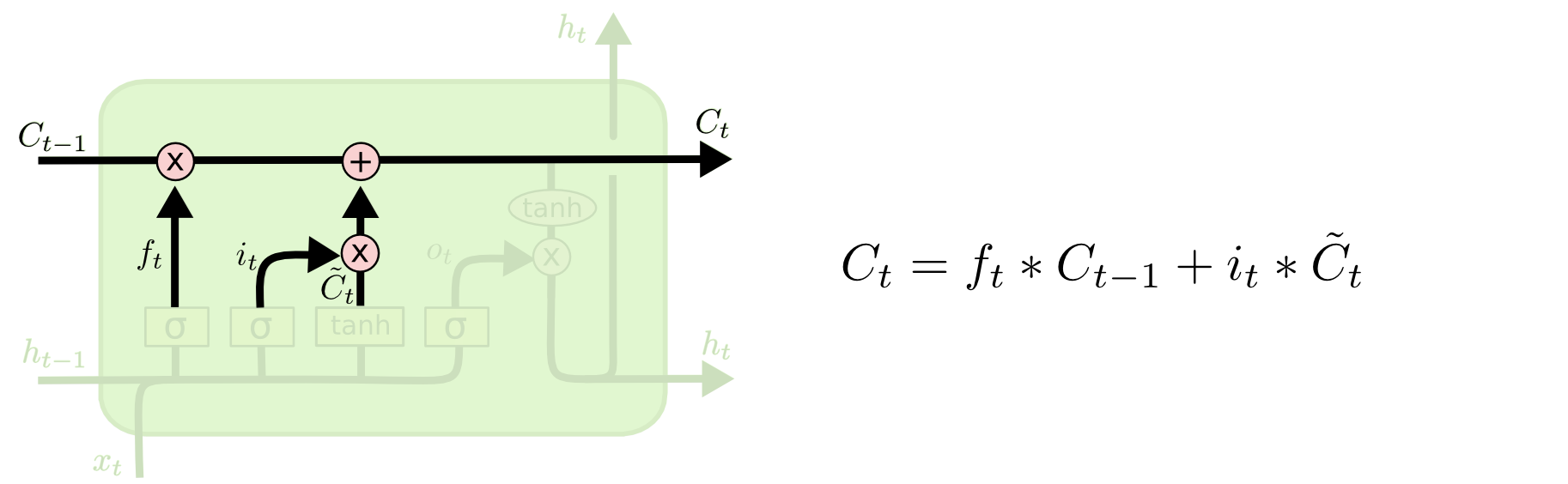
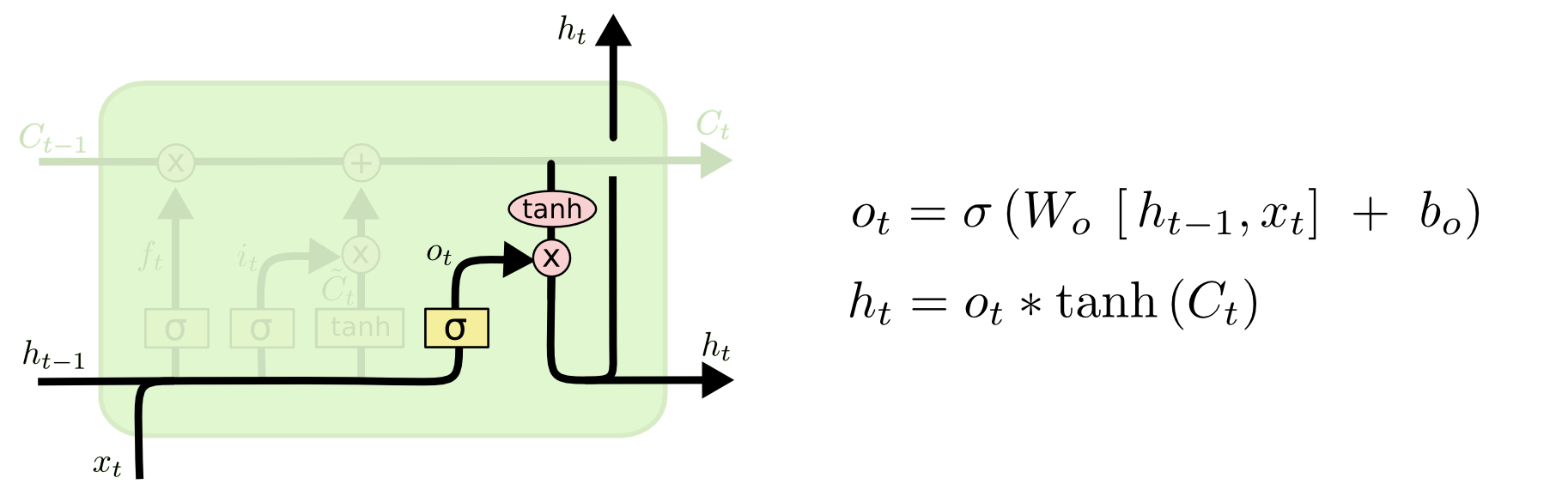
LSTM(
LongShort-TermMemory) is technique to alleviate vanishing gradient throughgate adjustment:forget gate: generateforget ruleinput gate: generateremember ruleandcell state updatecell state:determinehow much to remember and how much to forgetoutput gate: generatehidden stateandoutput
-
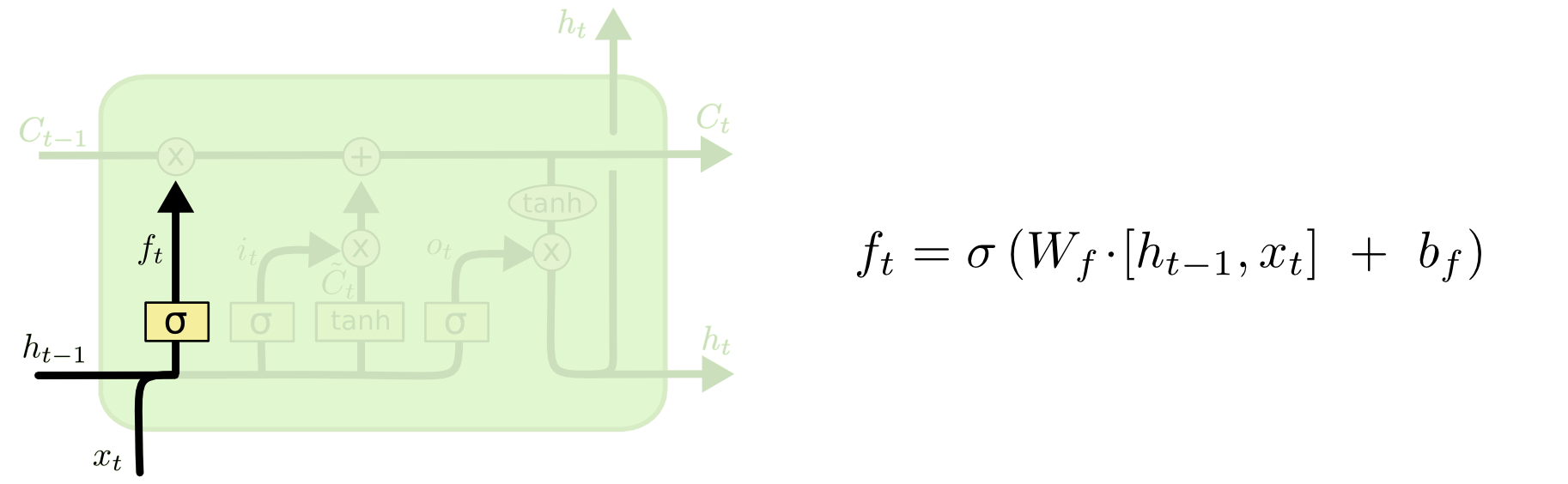
forget gate:
-
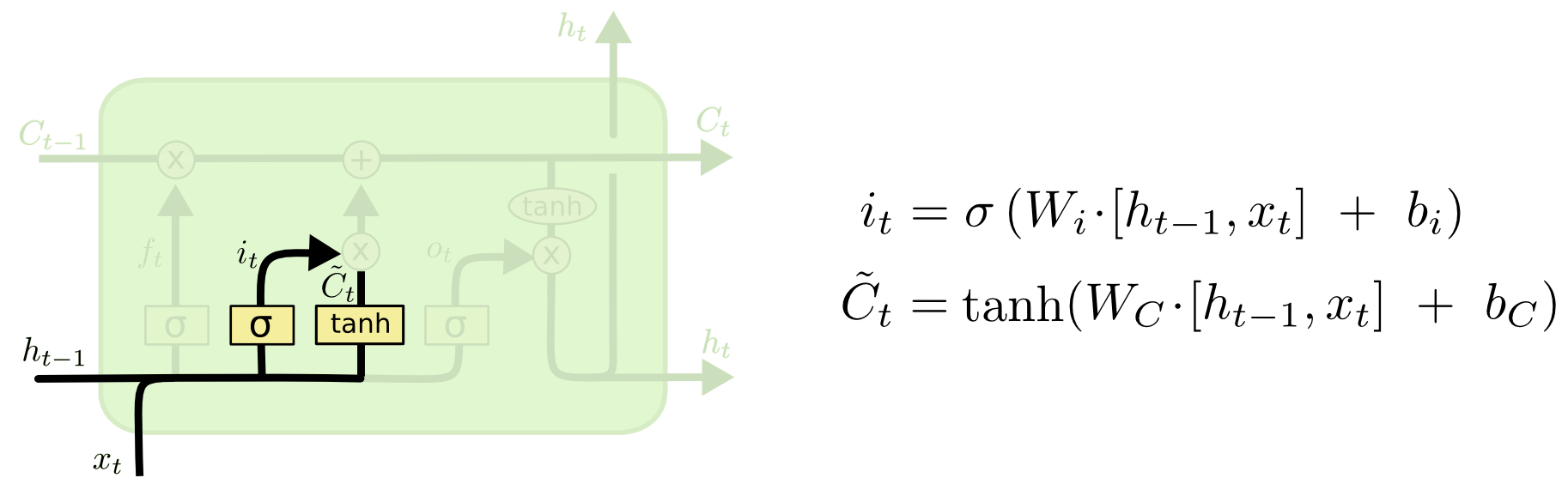
input gate:
-
cell state:
-
output gate:
Sourse
- https://dgkim5360.tistory.com/entry/understanding-long-short-term-memory-lstm-kr