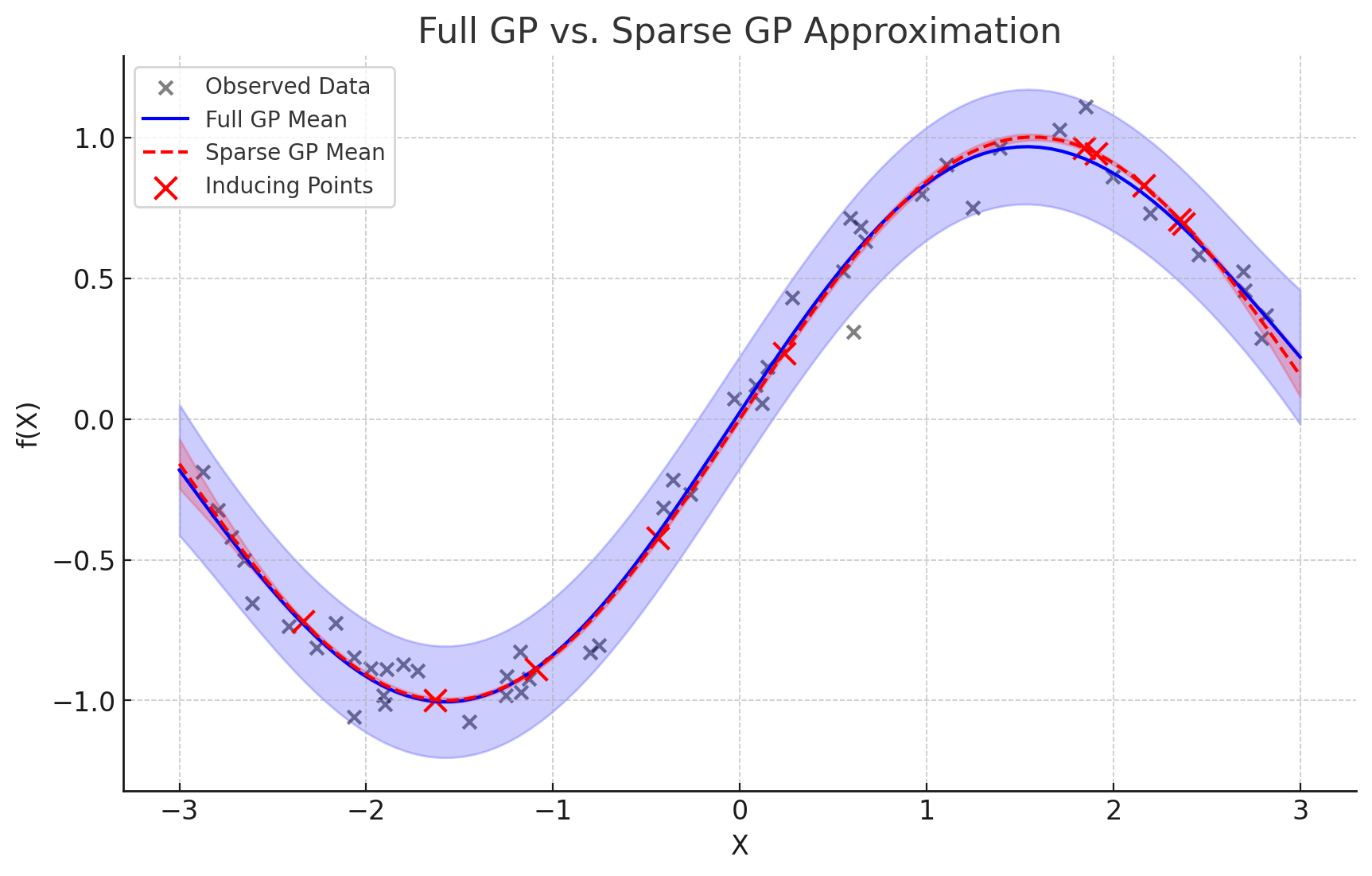
Sparse Gaussian Process
GP
-
가우시안 프로세스(
\[\begin{aligned} f(\cdot) \sim \mathcal{GP}(\mu(\cdot), \mathcal{K}(\cdot, \cdot)) \end{aligned}\]GaussianProcess): 순차 입력 $x_{1},x_{2},\cdots \in \ell^{2}$ 에 대한 출력 $f(x_{1}),f(x_{2}),\cdots \in \ell^{2}$ 이 입력 공간 $\ell^{2}$ 전체에 대하여 확률 분포를 가지는 확률 과정으로서, 함수 자체를 확률변수로 취하는 함수 분포 -
$f(x) \sim \mathcal{N}(\mu(x),\mathcal{K}(x,x))$: 입력값 $x$ 에 대한 출력값
\[\begin{aligned} f(x) \in \ell^{2} \end{aligned}\] -
$\mathbf{f} \sim \mathcal{N}(\mu,\Sigma)$: 입력값 $x_{1},x_{2},\cdots$ 에 대한 출력값 $f(x_{1}),f(x_{2}),\cdots$ 벡터
\[\begin{aligned} \mathbf{f} := \begin{bmatrix} f(x_{1})\\ f(x_{2})\\ \vdots \end{bmatrix} \in \ell^{2} \end{aligned}\]-
$\mu$: 입력값 $x_{1},x_{2},\cdots$ 에 대한 출력값 $f(x_{1}),f(x_{2}),\cdots$ 의 평균 벡터
\[\begin{aligned} \mu =\begin{bmatrix} \mu(x_{1}) \\ \mu(x_{2}) \\ \vdots \end{bmatrix} \end{aligned}\] -
$\Sigma$: 입력값 $x_{1},x_{2},\cdots$ 에 대한 출력값 $f(x_{1}),f(x_{2}),\cdots$ 의 공분산 행렬
\[\begin{aligned} \Sigma &=\begin{bmatrix} \mathcal{K}(x_{1},x_{1}) & \mathcal{K}(x_{1},x_{2}) & \cdots \\ \mathcal{K}(x_{2},x_{1}) & \mathcal{K}(x_{2},x_{2}) & \cdots \\ \vdots & \vdots & \ddots \end{bmatrix} \end{aligned}\]
-
-
$f(\cdot) \sim \mathcal{GP}(\mu(\cdot), \mathcal{K}(\cdot, \cdot))$: $\forall x$ 에 대하여 $f(\forall x)$ 를 정의하는 규칙
\[\begin{aligned} f(\cdot) \in \mathcal{H}_{\mathcal{K}} \end{aligned}\]
SGP
-
SGP(
SparseGaussianProcess) : $M < N$ 개의 유도점(Inducing Points)을 도입하여 공분산 행렬을 근사하는 기법으로서, 계산량을 $\mathcal{O}(N^{3}) \to \mathcal{O}(M^{2}N)$ 으로 줄임으로써 효율성을 도모함 -
Methods
- Nyström Approximation
BASIC- Inducing Points Sampling
- Matrix Factorization
- FITC(
FullyIndependentTrainingConditional)- Inducing Points Sampling
- All data Points are Independent of the Inducing Points
- Matrix Factorization
- SKI(
StructuredKernelInterpolation)- Grid based Inducing Points
- Matrix Factorization
- SVGP(
SparseVariationalGaussianProcess)- Inducing Points Optimization
- Variational Inference
- DGP(
DecoupledGaussianProcess)- Separate the Inducing Points into Mean Function and Covariance Function
- Mean Function and Covariance Function Optimization
- Variational Inference
- Nyström Approximation
Nyström Approximation
-
Matrix Factorization
\[\begin{aligned} \mathbf{K}_{N} \approx \mathbf{Q}_{N} = \mathbf{K}_{NM} \cdot \mathbf{K}^{-1}_{MM} \cdot \mathbf{K}_{MN} \end{aligned}\]- \(\mathbf{K}_{MM}\) : 유도점끼리의 공분산 행렬
- \(\mathbf{K}_{NM}\) : 전체 데이터와 유도점 간 공분산 행렬
- \(\mathbf{K}_{MN}\) : \(\mathbf{K}_{NM}\) 의 전치 행렬
-
Posterior Dist.
\[\begin{aligned} \mathcal{F}^{*} \mid X, Y, X^{*} \sim \mathcal{N}(\mu^{*}, (\sigma^{*})^{2}) \end{aligned}\]-
Posterior Mean:
\[\begin{aligned} \mu^{*}=\mu(X^{*}) + \overrightarrow{\mathbf{q}}_{N}^{*}(\mathbf{Q}_{N}+\sigma^{2}_{N}\mathbf{I})^{-1}(Y-\mu(X)) \end{aligned}\] -
Posterior Var.:
\[\begin{aligned} (\sigma^{*})^{2} =\mathcal{K}(X^{*},X^{*})-\overrightarrow{\mathbf{q}}_{N}^{*}(\mathbf{Q}_{N}+\sigma^{2}_{N}\mathbf{I})^{-1}\left(\overrightarrow{\mathbf{q}}_{N}^{*}\right)^{T} \end{aligned}\]
-
Variational Inference based Opt.
-
SVGP(
SparseVariationalGaussianProcess)-
Variational Inference:
\[\begin{aligned} \log{p(Y \mid X)} \ge \mathbb{E}_{f \sim q}[\log{p(Y \mid f, X)}] - D_{KL}(q(f) \parallel p(f)) \end{aligned}\] -
$f$ 는 무한 차원의 확률 과정이므로 이를 직접 다루지 않고 유도점 $Z$ 와 이때의 함수 값 $u=f(Z)$ 를 이용하여 근사함:
\[\begin{aligned} \mathbb{E}_{f \sim q}[p(f \mid y, X)] &= \int{q(f) \cdot p(f \mid y, X)\text{d}f}\\ &\downarrow\\ \mathbb{E}_{u \sim q}[p(f \mid u, Z, X)] &= \int{q(u) \cdot p(f \mid u, Z, X)\text{d}u} \end{aligned}\]
-
-
DGP(
DecoupledGaussianProcess)