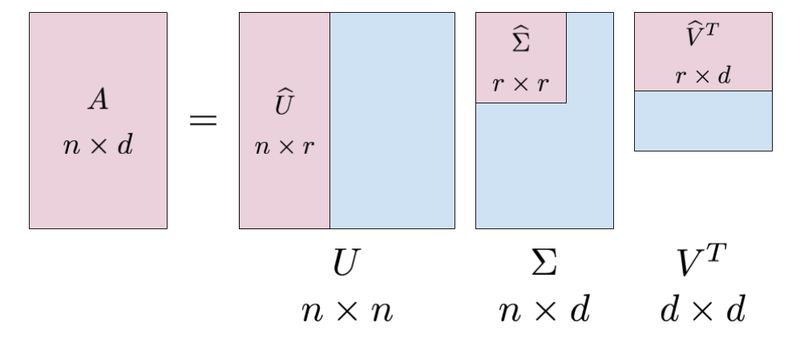Statistical Modeling Methods
Based on the lecture “Text Analytics (2024-1)” by Prof. Je Hyuk Lee, Dept. of Data Science, The Grad. School, Kookmin Univ.
Text Representation
Word Representation
Document Representation
-
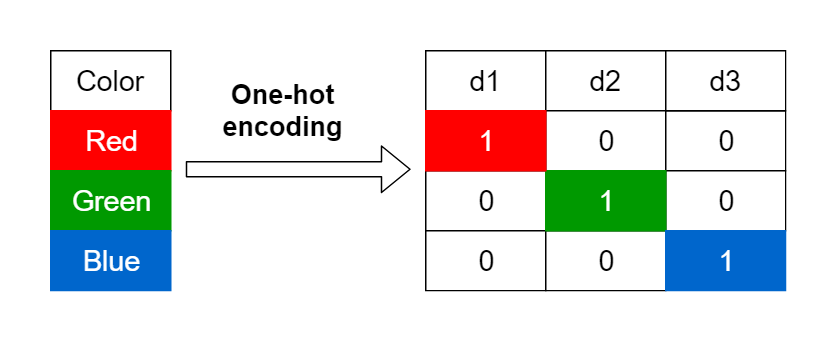
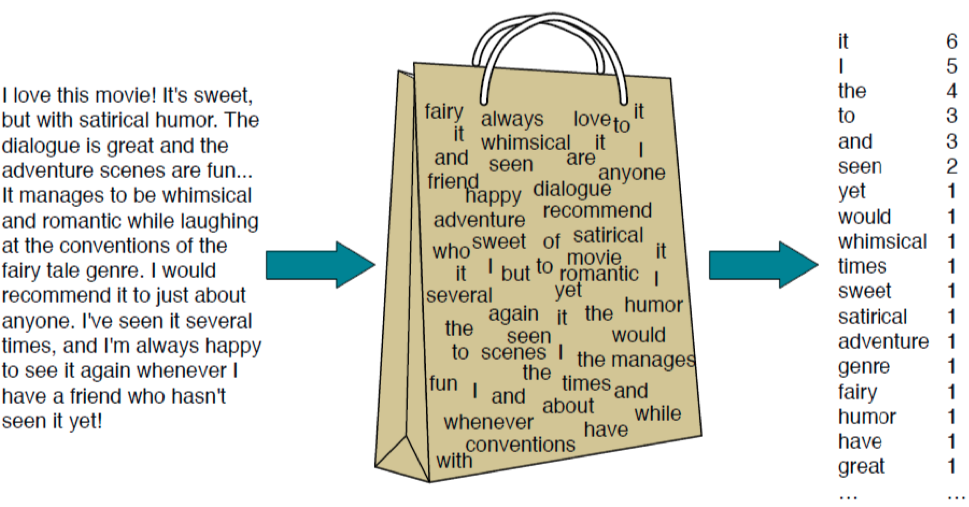
BoW(Bag of Words) : 문서를 단어 빈도 수로 표현하는 방법
-
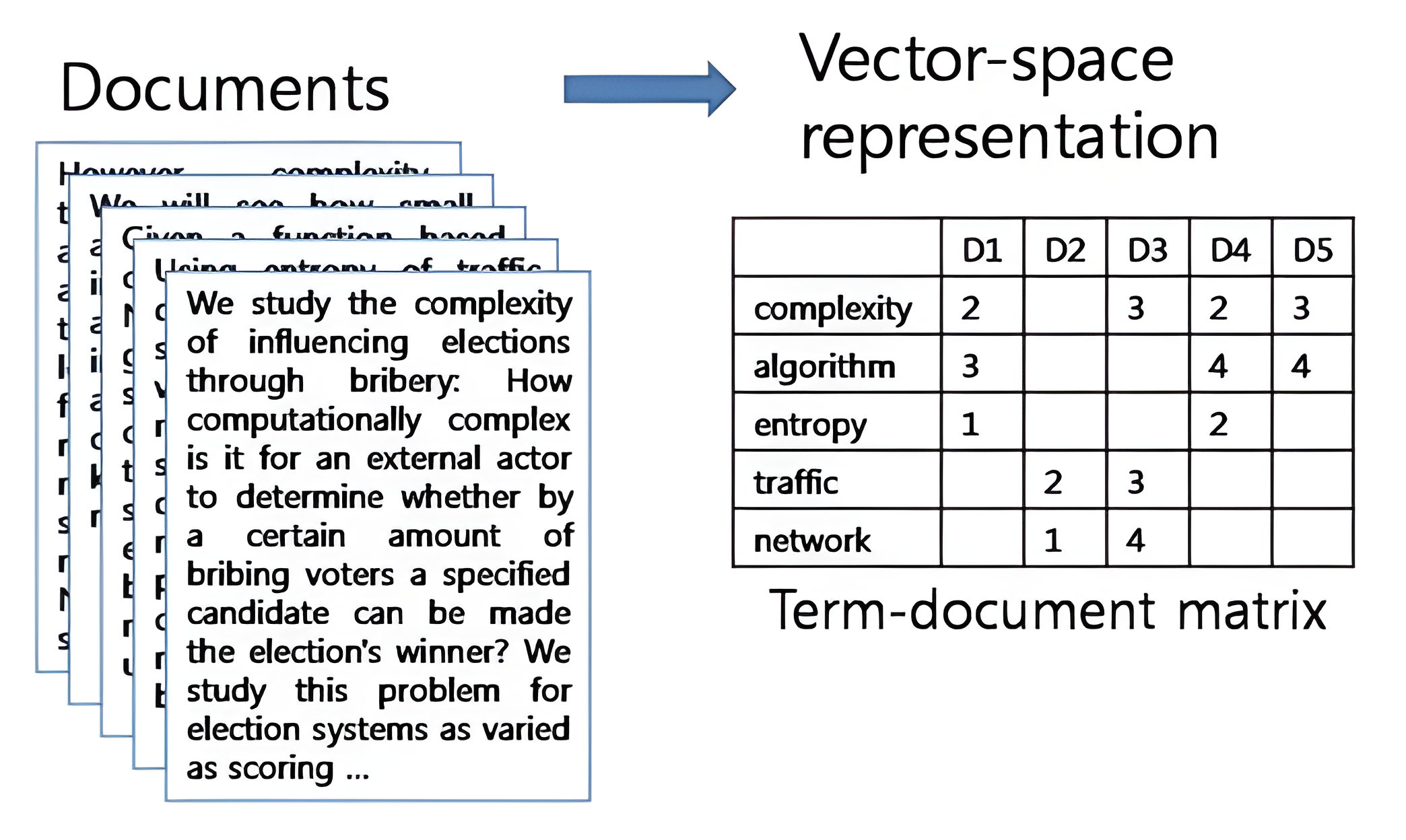
DTM(Document Term Matrix) : 여러 개의 문서를 BoW 로 표현하는 방법
-
TF-IDF(Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency) : DTM 내 단어들에 대하여 각 단어의 중요도에 따라 가중치를 부여하여 표현하는 방법
\[\text{TF-IDF}(d,t)=\text{TF}(d,t) \cdot \text{IDF}(t)\]-
TF(Term Frequency) : 문서 $d$ 에서 단어 $t$ 가 등장하는 횟수
\[\text{TF}(d,t)\] -
IDF(Inverse Document Frequency) : 단어 $t$ 가 등장하는 문서의 수에 반비례하는 수
\[\text{IDF}(t)=\ln{\frac{n}{1+\text{DF}(t)}}\]- $n$ : 문서의 수
- $\text{DF}(t)$ : 단어 $t$ 가 등장하는 문서의 수
-
Language Model
- 언어 모형(Language Model) : Word Sequence(문장)에 확률을 할당하여 가장 자연스러운 문장을 탐색하는 모형
SLM
-
Statistical Language Model(SLM) : 조건부 확률을 활용하여 Word Sequence 발생 확률을 부여하는 모형
\[\begin{aligned} P(W) &= P(w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_n)\\ &= \cancel{P(w_1)} \cdot \frac{\cancel{P(w_1,w_2)}}{\cancel{P(w_1)}} \cdot \frac{\cancel{P(w_1, w_2, w_3)}}{\cancel{P(w_1, w_2)}} \cdots \frac{P(w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_n)}{\cancel{P(w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_{n-1})}}\\ &= P(w_1) \cdot P(w_2 \mid w_1) \cdot P(w_3 \mid w_1, w_2) \cdots P(w_n \mid w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_{n-1})\\ &= \prod_{i=1}^{n}{P(w_i \mid w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_{i-1})} \end{aligned}\] -
확률 부여 방법
\[\begin{aligned} P(w_i \mid w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_{i-1}) &= \frac{\text{Count}(w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_i)}{\text{Count}(w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_{i-1})} \end{aligned}\]- $\text{Count}(w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_i)$ : 말뭉치에서 Word Sequence $(w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_i)$ 가 등장한 횟수
n-Gram
-
n-Gram : $i$ 번째 단어를 예측함에 있어 $N-1$ 개의 단어만을 활용하는 모형
\[\begin{aligned} P(W) &= \prod_{i=1}^{n}{P(w_{i} \mid w_{i-(n-1)}, w_{i-(n-2)}, \cdots, w_{i-1})} \end{aligned}\] -
How to Select $n$ : 통상 $n \le 5$ 권장
Problem Small $n$ Large $n$ Sparsity Problem $\downarrow$ $\uparrow$ Long-term Dependency $\uparrow$ $\downarrow$ - 희소성 문제(Sparsity Problem) : 충분한 데이터를 관측하지 못하여 언어를 정확히 모델링하지 못하는 문제
- 장기 의존성 문제(Long-term Dependency) : 문맥 내에서 멀리 떨어져 있는 단어들 간의 관계를 처리하는 문제
PPL
-
Perplexity(PPL) : 언어 모형의 성능 평가 지표
\[\begin{aligned} PPL(W) &= P(W)^{-\frac{1}{N}}\\ &= P(w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_N)^{-\frac{1}{N}}\\ &= \sqrt[N]{\frac{1}{P(w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_N)}}\\ &= \sqrt[N]{\frac{1}{\prod_{i=1}^{n}{P(w_N \mid w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_{N-1})}}} \end{aligned}\] -
해석 : 선택 가능한 경우의 수를 의미하는 분기 계수(Branching Factor)로서, 특정 시점마다 평균적으로 고민하는 선택지 수
\[\begin{aligned} PPL(W) &=10\\ \sqrt[N]{\frac{1}{\prod_{i=1}^{n}{P(w_N \mid w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_{N-1})}}} &= 10\\ \prod_{i=1}^{n}{P(w_N \mid w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_{N-1})} &= \left(\frac{1}{10}\right)^{N}\\ \underset{\frac{1}{10}}{P(w_1)} \cdot \underset{\frac{1}{10}}{P(w_2 \mid w_1)} \cdot \underset{\frac{1}{10}}{P(w_3 \mid w_1, w_2)} \cdots \underset{\frac{1}{10}}{P(w_N \mid w_1, w_2, \cdots, w_{N-1})} &= \left(\frac{1}{10}\right)^{N} \end{aligned}\]
Topic Model
- 토픽 모형(Topic Model) : 관측 가능한 단어(Word) 및 문서(Document)로부터 말뭉치(Corpus)에 내재되어 있는(Latent) 토픽(Topic)을 탐색하는 방법
- 문서(Document)는 토픽(Topic)으로 어떻게 표현할 수 있을까?
- 단어(Word)는 토픽(Topic) 별로 어떻게 등장하는가?
- 탐색된 Something(Topic)의 정체를 무엇이라 정의하면 좋을까?
LSA
-
잠재 의미 분석(Latent Semantic Analysis; LSA) : 특이값 분해(Singular Value Decomposition; SVD)를 활용하여 Document-Term Matrix 를 분해하는 방법
\[\mathbb{A}_{n \times d} \approx \mathbb{U}_{n \times k} \cdot \Sigma_{k \times k} \cdot \mathbb{V}^{T}_{d \times k}\]Dimension Interpretation $n$ Number of Document $d$ Number of Term $k$ Number of Topic Hyper-Parameter - $\mathbb{A}_{n \times d}$ : Document-Term Matrix
- \(\mathbb{U}_{n \times k} \cdot \Sigma_{k \times k}\) : Document-Topic Matrix
- $\Sigma_{k \times k} \cdot \mathbb{V}_{d \times k}^{T}$ : Term-Topic Matrix
SVD
-
특이값 분해(Singular Value Decomposition; SVD) : 차원의 크기가 $n \times d$ 인 임의의 행렬 $\mathbb{A}$ 를 세 개의 행렬의 곱으로 분해하는 방법
- $\mathbb{U}_{n \times k}$ : 직교 정규 행렬(Ortho-normal Matrix)
-
열벡터 $\overrightarrow{u}_{i} \in \mathbb{U}$ 는 행렬 $\mathbb{A} \cdot \mathbb{A}^{T}$ 의 고유벡터(Eigen Vector)임
\[\mathbb{A}\mathbb{A}^{T} \cdot \overrightarrow{u}_i = \lambda_i \overrightarrow{u}_i\] -
열벡터 $\overrightarrow{u}_{i}$ 의 길이는 $1$ 임
\[\Vert \overrightarrow{u}_{i} \Vert = 1\] -
열벡터 \(\overrightarrow{u}_{i}, \overrightarrow{u}_{j}\) 은 직교함
\[\overrightarrow{u}_{i} \perp \overrightarrow{u}_{j} \Leftrightarrow \langle \overrightarrow{u}_{i}, \overrightarrow{u}_{j} \rangle = 0\]
-
- $\mathbb{V}_{d \times k}^{T}$ : 직교 정규 행렬(Ortho-normal Matrix)
-
열벡터 $\overrightarrow{v}_{i} \in \mathbb{V}$ 는 행렬 $\mathbb{A}^{T} \cdot \mathbb{A}$ 의 고유벡터(Eigen Vector)임
\[\mathbb{A}^{T}\mathbb{A} \cdot \overrightarrow{v}_i = \lambda_i \overrightarrow{v}_i\] -
열벡터 $\overrightarrow{v}_{i}$ 의 길이는 $1$ 임
\[\Vert \overrightarrow{v}_{i} \Vert = 1\] -
열벡터 \(\overrightarrow{v}_{i}, \overrightarrow{v}_{j}\) 은 직교함
\[\overrightarrow{v}_{i} \perp \overrightarrow{v}_{j} \Leftrightarrow \langle \overrightarrow{v}_{i}, \overrightarrow{v}_{j} \rangle = 0\]
-
-
$\Sigma_{k \times k}$ : 대각 행렬(Diagonal Matrix)
\[\Sigma_{k \times k} = \begin{pmatrix} \sigma_{1} & 0 & \cdots & 0 \\ 0 & \sigma_{2} & \cdots & 0 \\ \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\ 0 & 0 & \cdots & \sigma_{k} \end{pmatrix}\]-
대각항의 원소 $\sigma_{i}$ 는 행렬 $\mathbb{A} \cdot \mathbb{A}^{T}$ 혹은 $\mathbb{A}^{T} \cdot \mathbb{A}$ 의 고유값(Eigen Value) $\lambda_{i}$ 의 자승근임
\[\sigma_{i} = \sqrt{\lambda_i}\]
-
LDA
-
잠재 디리클레 할당(Latent Dirichlet Allocation; LDA) : 베이지안 프레임워크를 활용하여 문서에 내재된 잠재적인 토픽 구조를 탐색하는 방법
\[\begin{aligned} &\hat{\theta}, \hat{\psi}\\ &=\text{arg} \max_{\theta, \psi}{\prod_{d=1}^{D}{\prod_{n=1}^{N_d}{P(\theta_d, \psi_{z(d,n)}; z(d,n) \mid w(d,n))}}}\\ &\propto \text{arg} \max_{\theta, \psi}{\prod_{d=1}^{D}{\prod_{n=1}^{N_d}{P(\theta_d \mid z(d,n)) \times P(\psi_{z(d,n)} \mid w(d,n))}}}\\ &\propto \text{arg} \max_{\theta, \psi}{\prod_{d=1}^{D}{\prod_{n=1}^{N_d}{\underbrace{P(\theta_d) \cdot P(z(d,n) \mid \theta_d)}_{\begin{array}{c} \text{Document-Topic} \\ \text{Allocation} \end{array}} \times \underbrace{P(\psi_{z(d,n)}) \cdot P(w(d,n) \mid \psi_{z(d,n)})}_{\begin{array}{c} \text{Topic-Word} \\ \text{Allocation} \end{array}}}}} \end{aligned}\]- $P(\theta_d \mid z(d,n)) \propto P(\theta_d) \cdot P(z(d,n) \mid \theta_d)$ : Posterior Probability of Document-Topic Allocation
- $P(\psi_{z(d,n)} \mid w(d,n)) \propto P(\psi_{z(d,n)}) \cdot P(w(d,n) \mid \psi_{z(d,n)})$ : Posterior Probability of Topic-Word Allocation
Posterior Probability
각 문서는 여러 토픽의 혼합으로 구성되어 있고, 각 토픽은 특정 단어들의 혼합으로 구성되어 있다고 가정하자. 특정 문서를 구성하고 있는 단어들로부터, 해당 단어들을 발생시킨 토픽들의 비중을 추론할 수 있음.
-
문서 $d$ 에는 여러 토픽들이 담겨 있으며, 각 토픽 발생 확률은 디리클레 분포를 따름
\[\begin{aligned} k \mid \theta_d &\sim \text{Multinomial}(\theta_{d})\\ \theta_{d} &\sim \text{Dirichlet}(\alpha) \end{aligned}\]- $k \mid \theta_d$ : 문서 $d$ 에서 토픽 $k$ 가 발생할 확률
- $\theta_d$ : $d$ 번째 문서에서 각 토픽들이 발생할 확률
-
토픽 $k$ 에서는 여러 단어들이 발생할 수 있으며, 각 단어 발생 확률은 디리클레 분포를 따름
\[\begin{aligned} w \mid \psi_{k} &\sim \text{Multinomial}(\psi_{k})\\ \psi_{k} &\sim \text{Dirichlet}(\beta) \end{aligned}\]- $w \mid \psi_{k}$ : 토픽 $k$ 에서 단어 $w$ 가 발생할 확률
- $\psi_{k}$ : 토픽 $k$ 에서 각 단어들이 발생할 확률
-
따라서 단어 $w(d,n)$ 이 발생했을 때, $\theta_d$ 및 $\psi_{z(d,n)}$ 의 사후 확률 분포는 다음과 같음
\[\begin{aligned} &P(\theta_d, \psi_{z(d,n)}; z(d,n) \mid w(d,n))\\ &\propto \underbrace{P(\theta_d \mid z(d,n))}_{\begin{array}{c} \text{Posterior of} \\ \text{Document-Topic} \\ \text{Allocation} \end{array}} \times \underbrace{P(\psi_{z(d,n)} \mid w(d,n))}_{\begin{array}{c} \text{Posterior of} \\ \text{Topic-Word} \\ \text{Allocation} \end{array}}\\ &\propto \left[\underbrace{P(\theta_d)}_{\text{Prior}} \cdot \underbrace{P(z(d,n) \mid \theta_d)}_{\text{Likelihood}}\right] \times \left[\underbrace{P(\psi_{z(d,n)})}_{\text{Prior}} \cdot \underbrace{P(w(d,n) \mid \psi_{z(d,n)})}_{\text{Likelihood}}\right] \end{aligned}\]- $w(d,n)$ : 문서 $d$ 의 $n$ 번째 단어
- $z(d,n)$ : 단어 $w(d,n)$ 에 대하여 해당 단어가 할당된 토픽
- $\theta_d$ : 문서 $d$ 의 토픽 분포
- $\psi_{z(d,n)}$ : 토픽 $z(d,n)$ 의 단어 분포
이미지 출처
- https://velog.io/@growthmindset/%EC%9B%90-%ED%95%AB-%EC%9D%B8%EC%BD%94%EB%94%A9One-Hot-Encoding
- https://intoli.com/blog/pca-and-svd/