Word Representation
Based on the lecture “Text Analytics (2024-1)” by Prof. Je Hyuk Lee, Dept. of Data Science, The Grad. School, Kookmin Univ.
Representation Methods
Sparse Representation
-
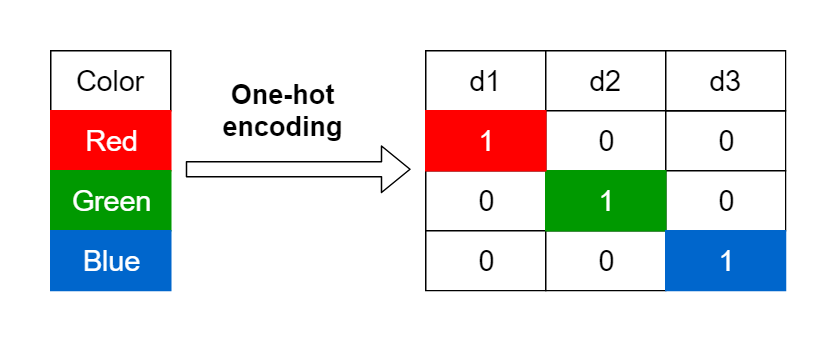
희소 표현(Sparse Representation) : 하나의 단어를 하나의 차원으로 하는 $n$ 차원 공간에 단어를 표현하는 방법
\[\begin{aligned} \text{Dog}&=\begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & \cdots \end{pmatrix}\\ \text{Puppy}&=\begin{pmatrix} 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & \cdots \end{pmatrix} \end{aligned}\]- Dimensionality Curse Problem in Sparse Vector
- Semantic/Structural Disjointness Problem
Dense Representation
-
단어 임베딩(Word Embedding) : 희소 표현의 한계점을 보완한 방법으로서, 분포 가설에 근거하여 단어를 밀집된 형태로 표현하는 방법
Embedding
An embedding is a mapping of a discrete - categorical - variable to a vector of continuous numbers.
In the context of machine learning, an embedding is a low-dimensional, learned continuous vector representation of discrete variables into which you can translate high-dimensional vectors. -
밀집 표현(Dense Representation) : 연구자가 설정한 $k \le n$ 차원 공간에 단어를 표현하는 방법
\[\begin{aligned} \text{Dog}&=\begin{pmatrix} 0.1 & 0.3 & -0.2 \end{pmatrix}\\ \text{Puppy}&=\begin{pmatrix} 0.1 & 0.3 & -0.3 \end{pmatrix} \end{aligned}\] -
분산 표현(Distributed Representation) : 분포 가설에 근거하여 단어의 의미 를 다차원 공간에 표현하는 방법
-
분포 가설(Distributional Hypothesis) : 비슷한 문맥에서 등장하는, 다시 말해 비슷하게 분포되어 있는 단어들은 비슷한 의미를 가짐
\[\begin{aligned} &\text{My dog is cute. Sometimes my dog braks at me.}\\ &\text{My puppy is cute. Sometimes my puppy braks at me.} \end{aligned}\]
-
WORD2VEC
- 워드 투 벡터(WORD2VEC) : 단어 임베딩 학습 방법론
- CBOW(
ContinuousBagofWords) : 주변 단어들로부터 중심 단어를 예측하는 과정에서 단어의 벡터 표현을 학습하는 방법론 - Skip-Gram : 중심 단어로부터 주변 단어들을 예측하는 과정에서 단어의 벡터 표현을 학습하는 방법론
- SGNS(
Skip-Gram withNegativeSampling) : Skip-Gram 에 Negative Sampling 을 적용함으로써 단어 예측 문제의 유형을 전환하는 방법론- Skip-Gram : 중심 단어가 등장했을 때 전체 단어가 발생할 확률 분포 학습 문제
- SGNS : 중심 단어가 등장했을 때 특정 주변 단어 발생 여부 판별 문제
- CBOW(
-
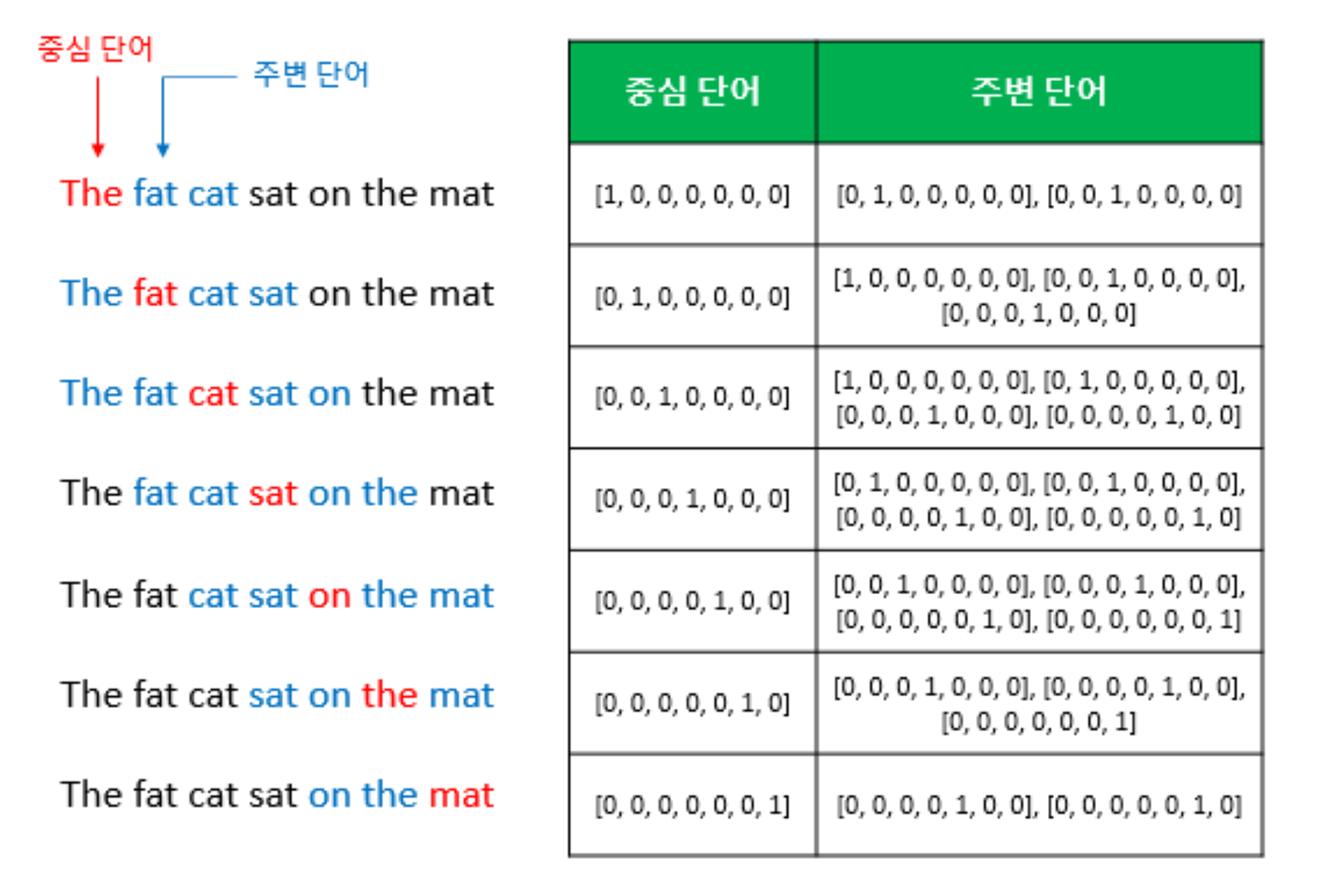
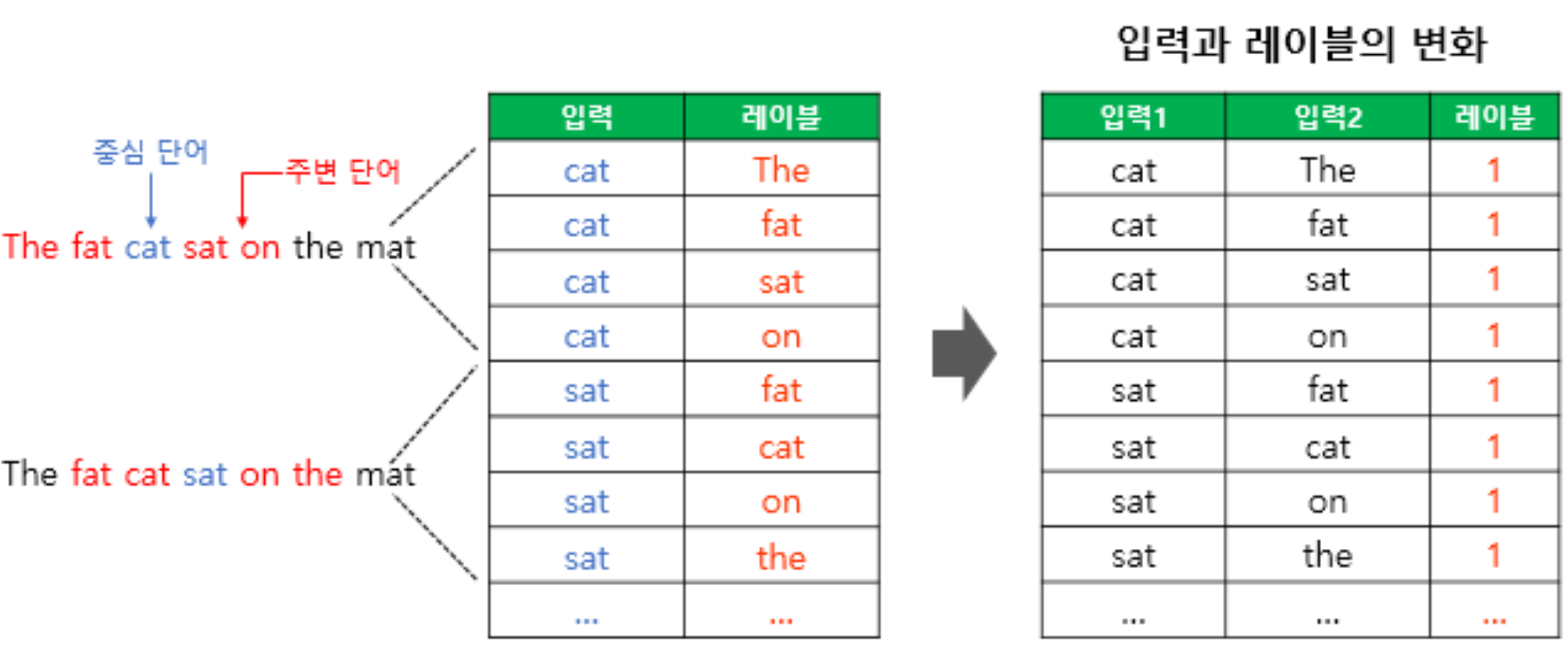
EXAMPLE“The fat cat sat on the mat” (Where Window Size is 2) - Annotation
- $\omega$ : Context Window Size
- $i$ : Target Word
- $j = 1,2,\cdots,\omega,\cdots,2\omega$ : Context Words
- $N$ : Number of Words
- $D$ : Embedding Size
- $\mathbf{X} \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times N}$ : One-Hot Encoded Matrix
- $\mathbf{W} \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times D}$ : Embedding Matrix
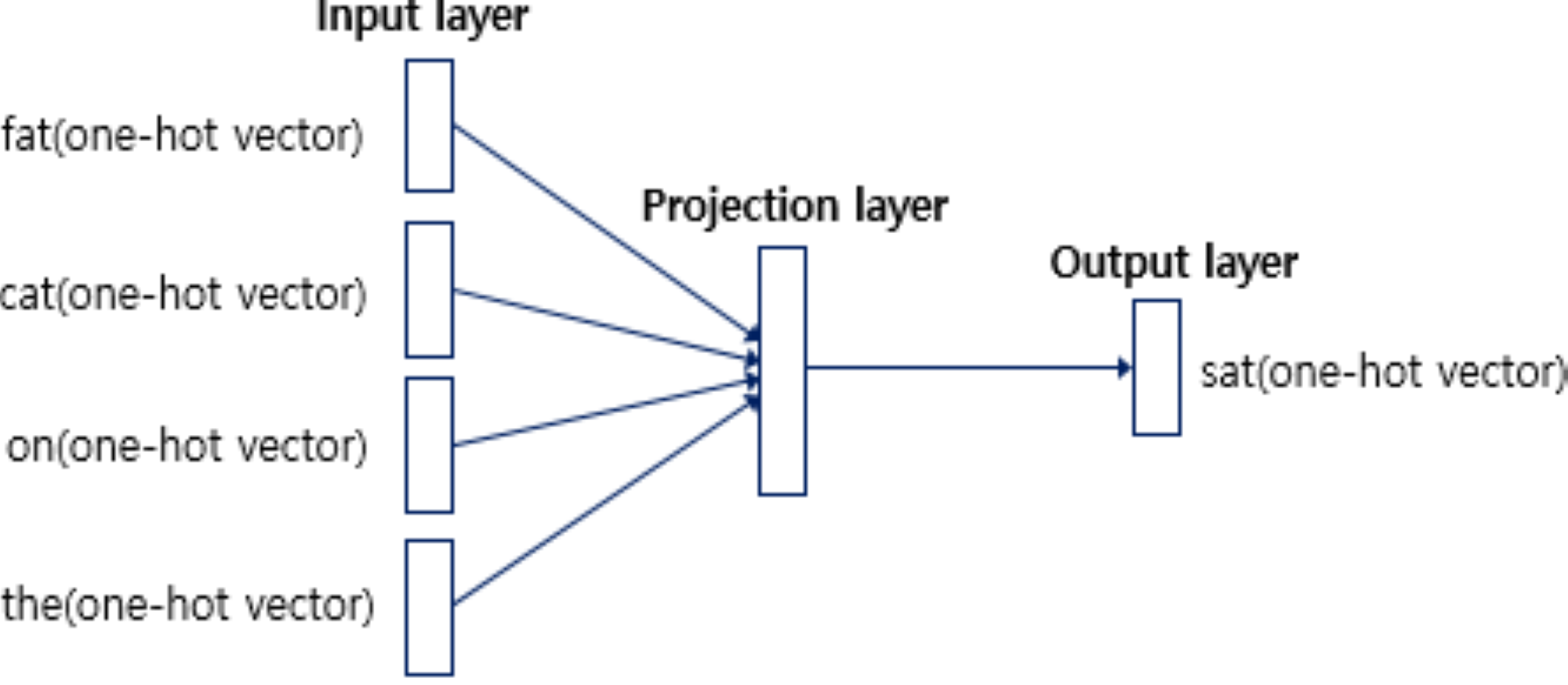
CBOW
-
\[\begin{aligned} \mathbf{z}_{i} &= \frac{1}{2 \omega} \sum_{j}{\mathbf{x}_{j} \cdot \mathbf{W}} \end{aligned}\]INPUT→PROJECTION- \(\mathbf{w}_{j} = \mathbf{x}_{j} \cdot \mathbf{W} \in \mathbb{R}^{D}\) : Embedding Vector of Context Word \(j\)
-
\[\begin{aligned} \hat{\mathbf{x}}_{i} &= \text{Softmax}\left[\mathbf{z}_{i} \cdot \mathbf{W}^{T}\right] \end{aligned}\]PROJECTION→OUTPUT -
Optimization
\[\begin{aligned} \hat{\mathbf{W}} &= \text{arg} \min{\sum_{i}{\text{Cross-Entropy}\left[\mathbf{x}_{i}, \hat{\mathbf{x}}_{i}\right]}} \end{aligned}\]
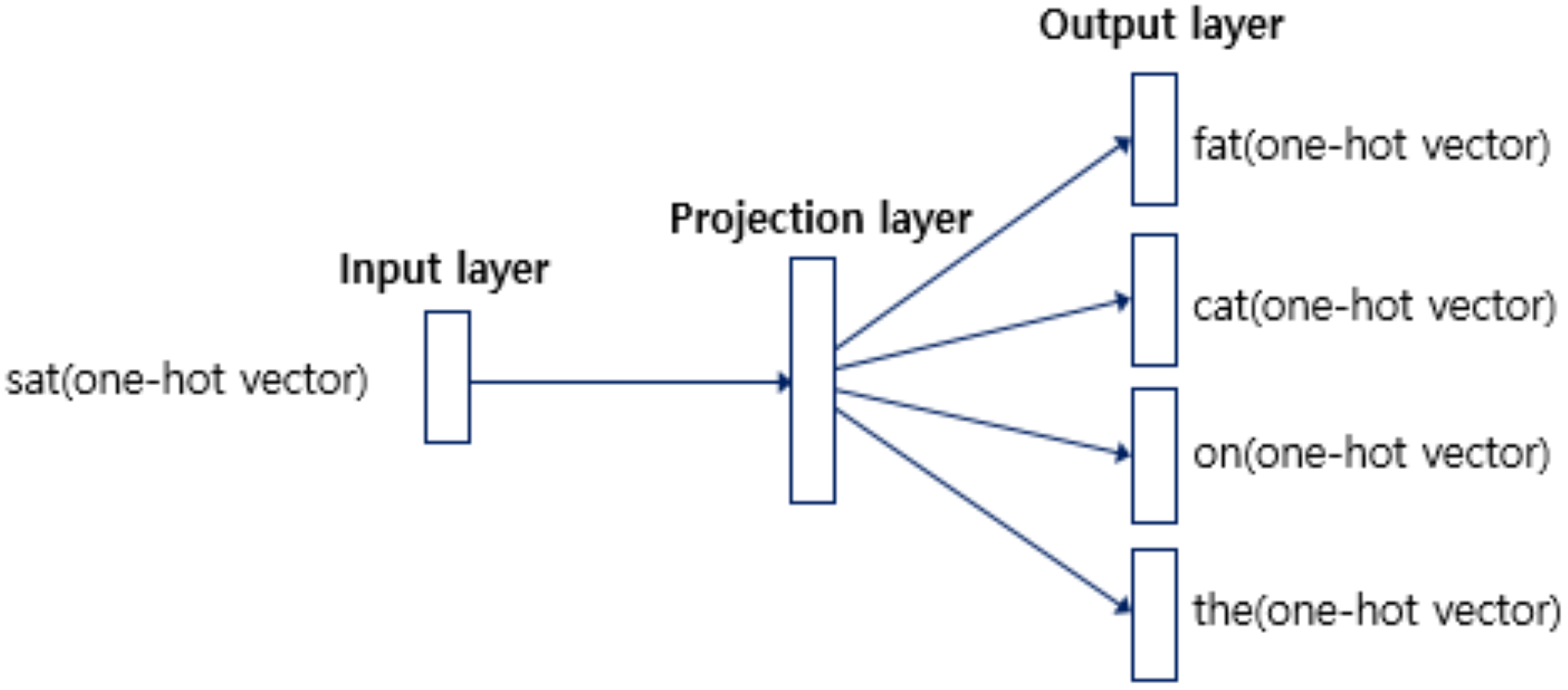
Skip-Gram
-
\[\begin{aligned} \mathbf{w}_{i} &=\mathbf{x}_{i} \cdot \mathbf{W} \end{aligned}\]INPUT→PROJECTION -
\[\begin{aligned} \mathbf{y}_{i} &= \text{Softmax}\left[\mathbf{w}_{i} \cdot \mathbf{W}^{T}\right] \end{aligned}\]PROJECTION→OUTPUT- \(\mathbf{y}_{i} \in \mathbb{R}^{N}\) : Context Probability Distribution Vector for Target Word $i$
-
Optimization
\[\begin{aligned} \hat{\mathbf{W}} &= \text{arg} \min{\sum_{i,j}{\text{Cross-Entropy}\left[\mathbf{x}_{j}, \mathbf{y}_{i}\right]}} \end{aligned}\]
SGNS
-
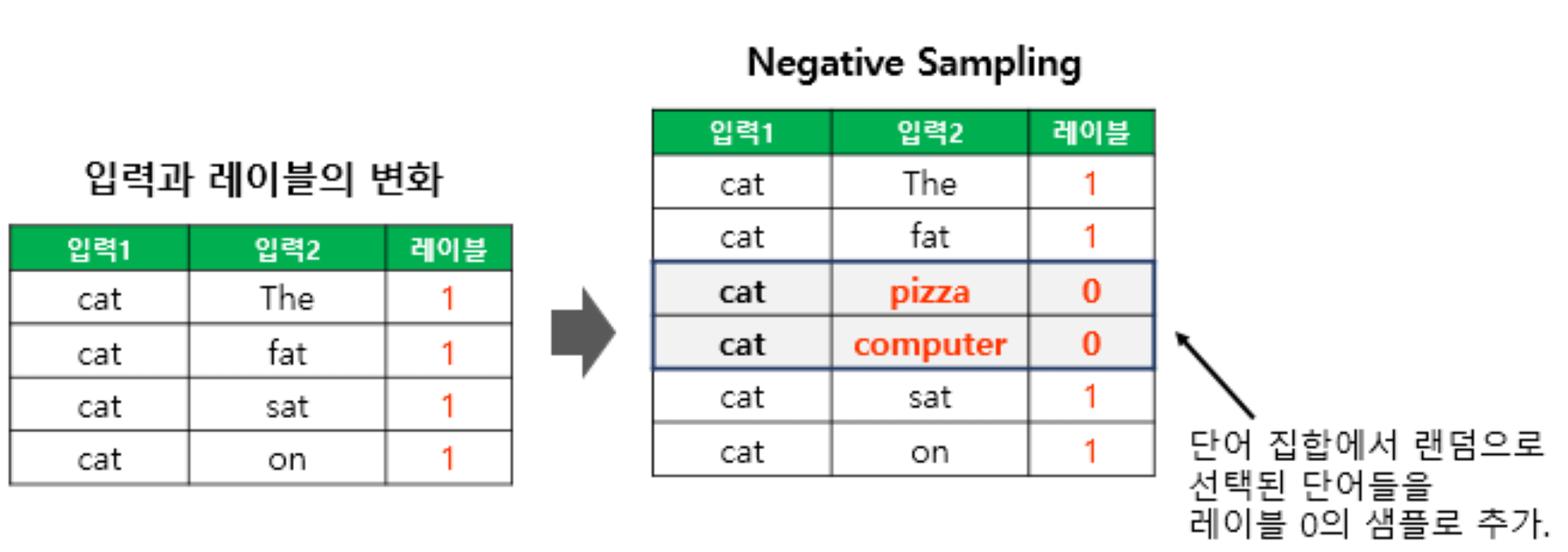
이진 분류 문제로 전환하기 위한 입력과 레이블 변화
-
Negative Sampling
-
$k$ 번째 단어가 샘플링될 확률
\[\begin{aligned} P\left(w_{k} \mid \alpha \right) &= \frac{f\left(w_{k}\right)^{\alpha}}{\sum_{l=1}^{N}{f\left(w_{l}\right)^{\alpha}}} \end{aligned}\]- $\alpha=0.75$ : 샘플링 확률 조정 파라미터로서 고빈도 단어가 샘플링될 확률을 할인함
- $f\left(w_{k}\right)$ : 통상 단어 빈도수로 설정함
-
-
Optimization
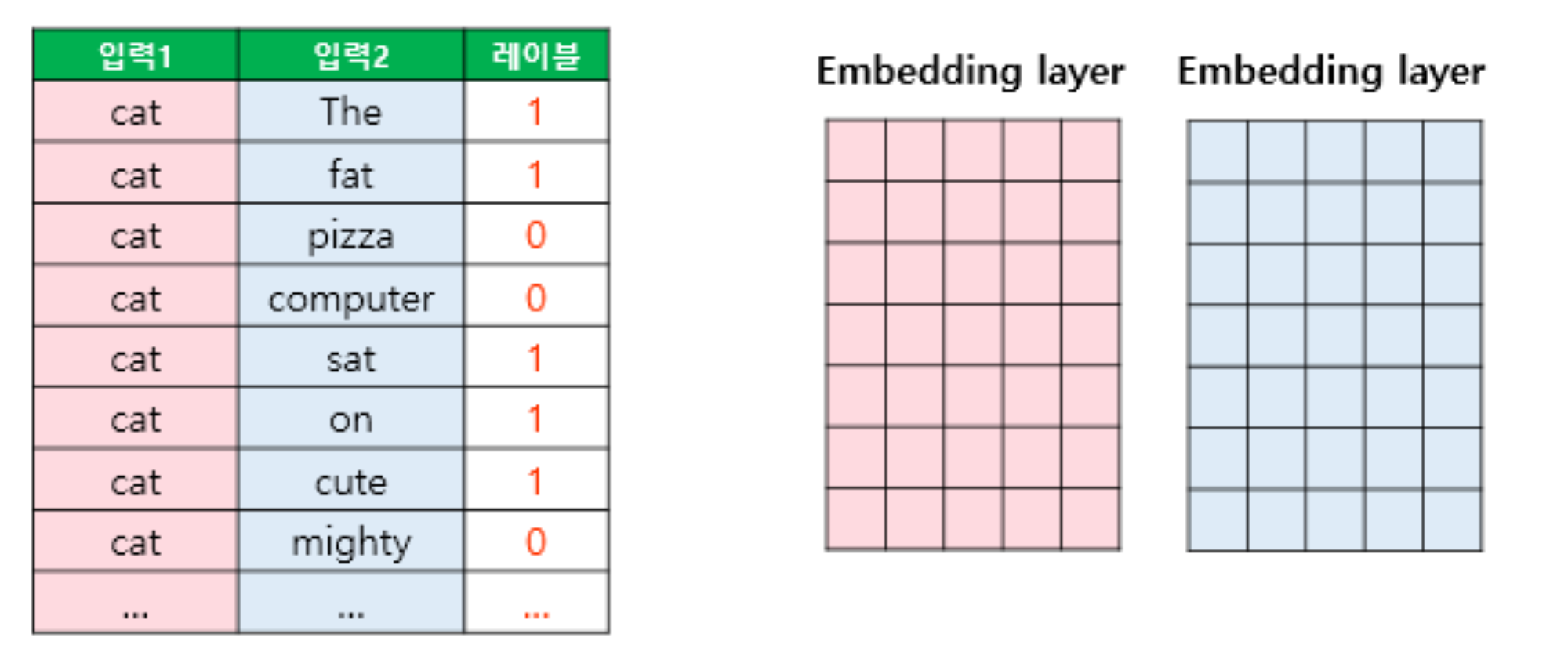
\[\begin{aligned} \hat{\mathbf{W}}, \hat{\mathbf{V}} &= \text{arg} \min{-\sum_{i,j}{y_{i,j} \log{\sigma\left[\mathbf{W}_{i} \cdot \mathbf{V}_{j}\right]} + \left(1-y_{i,j}\right) \log{\sigma\left[-\mathbf{W}_{i} \cdot \mathbf{V}_{j}\right]}}} \end{aligned}\]- $\mathbf{W} \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times D}$ : Target Embedding Matrix
- $\mathbf{V} \in \mathbb{R}^{N \times D}$ : Target Embedding Matrix
- $\sigma\left[\cdot\right]$ : Sigmoid Function
-
What? Final Embedding Matrix
- Target Embedding Matrix $\mathbf{W}$
- Concatenation $\mathbf{W} \oplus \mathbf{V}$
- Mean, Plus, etc.
Sourse
- https://velog.io/@growthmindset/%EC%9B%90-%ED%95%AB-%EC%9D%B8%EC%BD%94%EB%94%A9One-Hot-Encoding
- https://wikidocs.net/22660
- https://wikidocs.net/69141